Apple Is in a League of Its Own
During Apple’s “Peek Performance” event held last month, the company announced not only a brand new Mac category with the Mac Studio, but also iPhone SE and iPad Air updates that will be well-received in the marketplace. Management fit so much into its 57-minute event, Apple’s entry into live sports was given just 65 seconds.
The primary takeaway from Apple’s event wasn’t found with any particular product. Instead, it was the sheer breadth of product unveilings that caught my attention. Over the past 18 months, Apple has held seven jam-packed product unveilings that have included a collection of new hardware, software, and services. Apple’s peers would be thrilled to hold just one of these presentations every year or two. There is no other company in the same league as Apple when it comes to maintaining and updating such a wide and comprehensive ecosystem of devices and services. The pace of Apple’s new product unveilings has played a role in the company pulling away from the competition.
Ecosystem Strength
It's easy to look at Apple’s quarterly earnings and reach conclusions about the company’s ecosystem strength. Apple’s financials, although strong, don’t tell the full story. With nearly 80% of Apple’s revenue attributable to hardware, the company’s financials remain heavily influenced by upgrading trends. Revenue, operating income, and cash flow metrics undersell how Apple is performing in the marketplace from a new user perspective.
The following new user estimates are obtained by combining Apple management commentary with my own product unit sales assumptions:
To get to the heart of what Apple is doing and how the company is executing so well, we have to go back to 2017 and 2018. Apple began to follow a new strategy that amounted to pushing all of its product category forward at the same time. Previously, Apple had been following a product strategy that can be thought of as a pull system. The company was most aggressive with the products capable of making technology more relevant and personal.
One way of conceptualizing this strategy is to think of Apple product categories being attached to a rope in order of which makes technology more personal via new workflows and processes for getting work done. As Apple management pulled on the rope, the Apple Watch and iPhone received much of the attention while the Mac increasingly resembled dead weight. Similarly, the iPad had hit a rough patch.
Apple is now utilizing a push system in which every major product category is being pushed forward simultaneously. As a result, the iPad, and in particular the Mac, has received more priority. We have also since seen Apple become more aggressive with expanding the number of SKUs available and giving consumers more price and feature options.
At the core of Apple’s product strategy shift was a doubling down on autonomy within its product development process. The Apple machine is operating at such speed and scale, it’s not realistic to think one person can control or run the machine. Apple wouldn’t be able to push its entire product line forward simultaneously if every decision had to go through one gatekeeper. Instead, the Apple machine was designed to take on a certain level of autonomy in order to instill Apple’s values in all employees. Designers of various disciplines have been given greater say over the user experience.
Floundering Competition
As product strategy changes were underway within Apple, the competition began to flounder. A growing number of bad product bets were placed, peaking with the ultimate misdirection in tech of the past decade: voice computing and the stationary smart speaker mirage. The subsequent embrace of stationary screens positioned on kitchen countertops has seen limited adoption. Foldable smartphone sales have not been impressive. Apple competitors are now struggling to capture consumers’ attention and money with routine annual smartphone updates.
We are at the point when tough questions have to be asked about Apple’s competition, or lack thereof. What company can realistically give Apple a run for its money? The number of paid subscriptions across Apple’s platform is increasing by 170 million per year. Google wants to compete in some hardware verticals that Apple plays in, but it’s fair to question Google management’s commitment. At times, their heart just doesn’t seem in it. Amazon and Microsoft have stronger motivations to do well in hardware, but their lack of design thinking is hard to miss. Meta would win the award for strongest public commitment to hardware, but the company’s culture and heritage don’t seem to mesh well with what it takes to do well in hardware. Snap, Spotify, Sonos, and the long list of smaller companies dabbling in hardware all lack the ecosystems to truly go up against Apple toe to toe.
When thinking of competition outside the U.S., a growing number of consumers are looking for entry points into comprehensive (and premium) ecosystems. Apple is selling both the all-around best smartphone in the market and tools and services designed to live both below and above the smartphone. Android switching rates are increasing while Apple entices hundreds of millions of iPhone-only users to move deeper into the ecosystem.
A risk that any company in Apple’s position will face is complacency. With most of its product categories, Apple’s largest competitor ends up being itself. The fact that Apple’s ecosystem updates are accelerating rather than declining as the competition breaks apart is a potential sign of Apple decoupling itself from the “competition drives us” mantra that is found in Silicon Valley. There is a deeper drive within Apple – a feeling that if Apple doesn’t create it, no one else will - that is driving teams forward.
Check out the daily update from April 5th for additional discussion on this topic.
Receive Neil’s analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates. The updates, which have become widely read and influential in the world of Apple, provide timely analysis of news impacting Apple and its competitors. Neil also publishes exclusive reports on Apple business, product, and financial strategy. The daily updates and reports are available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
Above Avalon Year in Review (2021)
Heading into 2021, Apple had just gone through one of the more tumultuous years in its existence. As discussed in last year’s Year in Review, the pandemic turned 2020 into a steady stream of unexpected challenges for Apple. Expectations that 2021 would be much smoother turned out to be optimistic. While society did largely open up halfway through the year, which allowed Apple’s retail apparatus to return to normal operations, Apple continued to face once-in-a-few-decades challenges when it came to the supply chain, product manufacturing, and navigating its 154,000 employees through a pandemic.
According to my estimate, Apple experienced $10 billion of unmet demand in 2021 as a result of supply chain issues. This total is on top of lingering demand issues associated with wearables that arose from the pandemic.
Despite the challenges, 2021 was a record year for Apple on a number of business fronts:
Apple sold 260M+ iPhones - a record high for a 12-month period.
Apple sold 25M Macs - a record high for a 12-month period.
The Apple Watch installed base surpassed 100 million people.
Articles
In 2021, I published 10 Above Avalon articles. In looking through the articles, which are accessible to all, there was one overarching theme: Apple’s ecosystem continues to gain strength and is ready for the next major product category launch (a mixed reality headset).
Here are a few of my favorite articles published in 2021 (in no particular order):
Apple Has a Decade-Long Lead in Wearables. AssistiveTouch allows one to control an Apple Watch without actually touching the device. A series of hand and finger gestures can be used to control everything from answering a call to ending a workout. The technology is just the latest example of how Apple’s lead in wearables is still being underestimated. The evidence points to Apple having a wearables lead of not just a few years, but more like a decade.
Apple Won the Share Buyback Debate. I receive many questions about Apple from Above Avalon readers, listeners, and members. In previous years, one topic has been far ahead of any other as a source of questions. Everyone wanted to know about Apple’s share buyback program. Something interesting happened in 2020. I received far fewer questions about Apple’s share buyback program. To be precise, I didn’t receive an incoming question about buyback in nine months - from when the stock market put in a bottom in April 2020 to the start of 2021. What explains such a dramatic change? The Apple share buyback debate ended, and Apple was declared the winner.
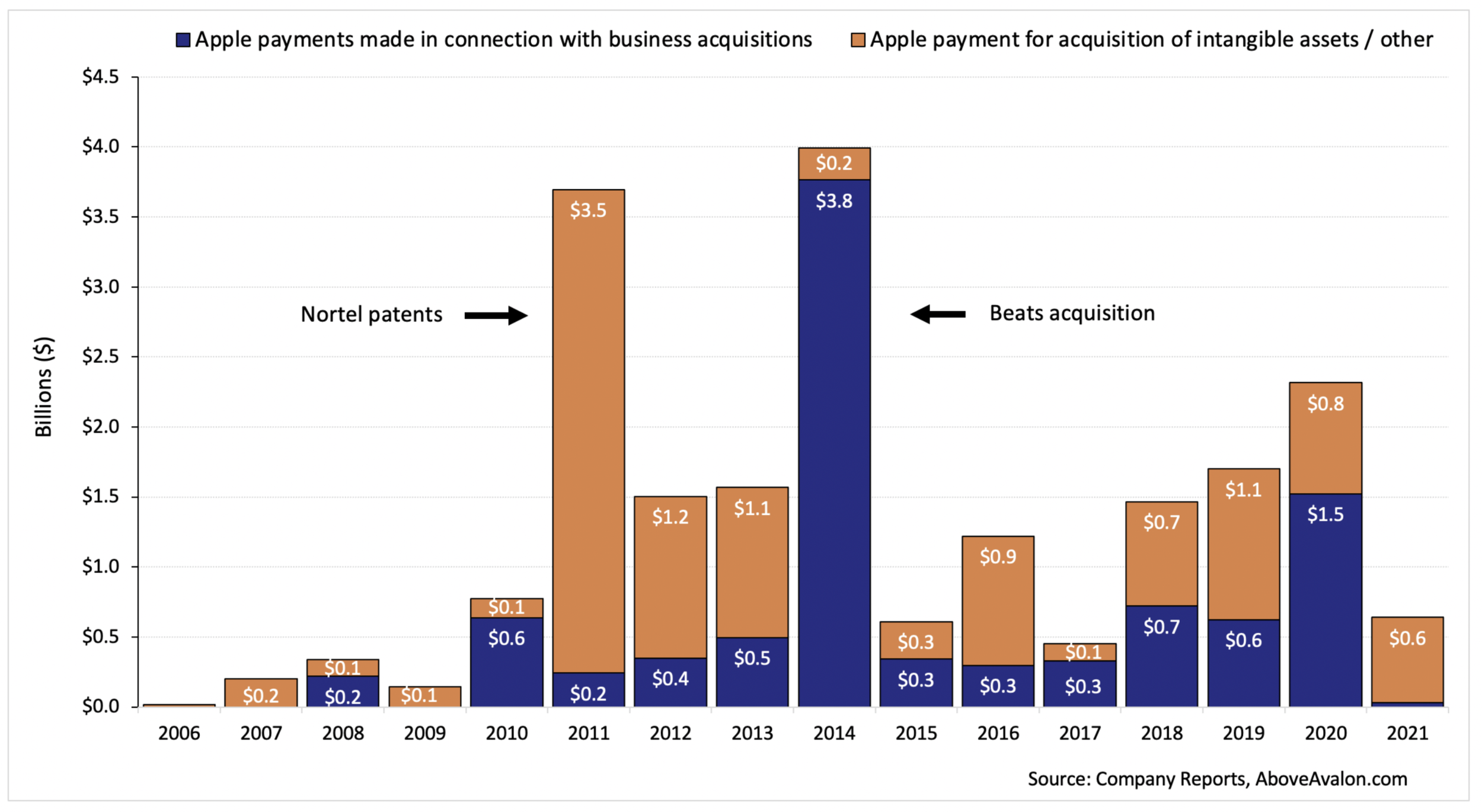
Apple’s Extremely Quiet Year for M&A. While going through Apple’s 10-K for FY2021, one number jumped out at me. It wasn’t the record iPhone sales, strong margins, or phenomenal free cash flow. Instead, it was the lack of cash spent on M&A. In 2021, Apple spent just $33 million on business acquisitions (M&A). That’s a record low for Apple with Tim Cook as CEO. It’s a number that deserves further investigation as Apple’s M&A strategy and philosophy play a big role in how Apple was able to get to where it is today.
The five most popular Above Avalon articles in 2021, as measured by page views, were:
Podcast Episodes
There were 11 episodes of the Above Avalon podcast recorded and published in 2021, totaling 4.5 hours. The podcast episodes that correspond to my favorite articles are found below:
Charts and Exhibits
The following charts and exhibits found in Above Avalon articles published in 2021 were among my favorites.
Apple Wearables Unit Sales (2017 to 2021) - from Apple Has a Decade-Long Lead in Wearables
According to my estimate, Apple is on track to sell 105 million wearable devices in 2021. That total represents 40% of the number of iPhones sold during the same time period. Unit sales don’t tell the full story, however. On a new-user basis, Apple is seeing more people enter the wearables arena than buy a new iPhone for the first time.
Note: Apple wearables include Apple Watch, AirPods, and select Beats headphones.
Percentage of Apple Revenue Through Direct Distribution Channel - from The Future of Apple Retail
The percentage of sales going through Apple’s direct distribution has gradually increased in recent years. The increase in sales percentage has likely been boosted by services revenue, more sales going through Apple’s website, and more iPhone upgrading taking place through Apple.
Note: Direct distribution channel includes Apple’s website, Apple stores, and direct sales force.
Apple M&A (Cash Payments) - from Apple’s Extremely Quiet Year for M&A
Since 2006, Apple has spent $20.6 billion on M&A with about half of the total tied to “business acquisitions.” The median is $1 billion per year. However, in 2021, Apple spent just $33 million on business acquisitions. That is the lowest amount since 2009 when Steve Jobs was still Apple CEO.
Daily Updates
In 2021, I published 182 Above Avalon Daily Updates that were available exclusively to Above Avalon members. With each update coming in at approximately 2,000 words, 182 updates are equivalent to five books. This continues to be an industry-leading number when it comes to the amount of Apple business and strategy analysis published.
When looking over the topics discussed in this year’s daily updates, a few sub themes become apparent:
Project Titan Moving Forward
Along with mixed reality and AR, transportation is one of the largest areas of opportunity when thinking of future Apple products and services. The year turned out to be the busiest one yet when it came to Project Titan news as Apple began to seek supply chain and manufacturing partners.
Hyundai Confirms Talks With Apple, Apple Considering Car Factory in Georgia, Making Sense of Apple and Hyundai News (Jan 12, 2021)
Apple Car and the Last Mile, Revisiting an Apple Campus Shuttle Service, Thursday Q&A (Feb 4, 2021)
Apple’s Kevin Lynch Joins Project Titan, Apple Car Implications, Apple Watch Implications (Jul 19, 2021)
Doug Field Leaves Apple for Ford, Project Titan’s Trajectory and Leadership, Silicon Valley vs. Detroit (Sep 8, 2021)
Kevin Lynch Tapped to Lead Project Titan, Disillusionment in the Auto Space Is Setting In, Ted Lasso Wins Big at the Emmys (Sep 20, 2021)
Changes in Paid Video Streaming Land
Given the rush of new players into the paid video streaming space in 2020, there was quite a bit of movement in 2021. AT&T’s decision to spin off WarnerMedia was an industry-shaking event. As the months went on, it became clear that many content distribution services were experiencing something equivalent to a pandemic air pocket as subscriber trends became noisy. Netflix and Roku ran into friction while the true new kid on the block (Apple TV+) regained momentum with new shows and movies coming online in the back half of the year.
AT&T to Spin Off WarnerMedia, HBO Max’s Future, Apple Implications May 17, 2021
WarnerDiscovery and Apple M&A, Ranking Paid Video Streaming Leaders, Netflix Contemplating Move into Gaming May 26, 2021
The App Store’s Day in U.S. Court
The well-publicized Epic Games vs. Apple trial resulted in a resounding legal victory for Apple. It ended up being difficult to grasp just how poor of a job Epic Games did in trying to paint Apple as a monopoly. While the court did order Apple to change its anti-steering provision in the U.S., Apple won a stay by a court of appeals. The outcome with the highest probability is for the anti-steering provision to remain as is which would signal Apple’s very strong legal footing as it pertains to the App Store.
Epic Games vs. Apple, Epic's Arguments Against Apple, Epic’s Motivation Apr 27, 2021
Thoughts on the Epic Games vs. Apple Ruling Sep 13, 2021
When looking at my daily updates published in 2021, selecting a few favorites out of 196 updates was not easy. The following updates stood out to me (in no particular order):
Warren Buffett’s Annual Letter, Apple Isn’t Buffett’s Token “Tech” Stock, Apple, Buffett, and Buyback. We kick off today’s update with my thoughts on Warren Buffett’s 2020 letter to Berkshire Hathaway shareholders. Berkshire is Apple’s largest individual shareholder. The discussion then turns to why I don’t agree with those claiming Apple is Buffett’s token tech stock. We conclude by looking at share buyback and how the capital return mechanism leads to a wealth transfer event. (Mar 2, 2021)
Peloton Recalls All of Its Treadmills, The At-Home Fitness Revolution Needs a Reset, Apple, Fitness Machines, and Gyms. Today’s update will be focused on the at-home fitness industry. It’s a market that Apple moved deeper into a few months ago with Apple Fitness+. A good argument can be made that at-home fitness impacts other Apple devices as well especially Apple Watch and Apple TV. We kick things off with my thoughts on Peloton recalling all of its treadmills. The discussion then turns to why I think the at-home fitness industry needs a reset. The update concludes with how fitness equipment safety, or the lack thereof, impacts Apple and why I continue to think there will be a role for gyms to play in the future. (May 6, 2021)
Tesla Buys Bitcoin, Apple and Bitcoin, Apple and Crypto Exchanges. Today’s update will be focused on bitcoin. We begin with news of Tesla buying $1.5B of bitcoin. We then turn to my thoughts on whether or not Apple should follow Tesla into bitcoin. The update concludes with a closer look at RBC Capital Market’s suggestion that Apple should move into cryptocurrency exchanges. We go over why I don’t think the firm’s analysis passes the small test. (Feb 10, 2021)
Apple’s Services Journey, A Different Way of Thinking of Apple One, Apple Services Evolution. For the first time in what feels like a long time, the Apple news cycle is taking a breather. This provides us with an opportunity to pursue some original topics. We kick off today’s update with my thoughts on the narrative surrounding Apple’s Services business. Things are starting to change. The discussion then turns to how I think about Apple’s Apple One bundle and how reframing Apple One leads to some interesting questions and ideas as it pertains to the competition. The update concludes with my thoughts on the future factors determining where Apple Services are headed. (Jul 13, 2021)
Niantic CEO Pours Cold Water on the Metaverse, Meta Buys Within, The Mistake People Are Making With the Metaverse. We kick things off with my thoughts on Niantic CEO John Hanke’s interview with The Verge’s Nilay Patel on his Decoder podcast. Hanke discussed some of the more intriguing topics and concepts found in the AR/VR/metaverse space. The discussion then turns to Meta (Facebook) buying Within. We go over two items that jumped out at me about the acquisition. The update concludes with the mistake that I see consensus making when it comes to metaverse analysis. (Dec 16, 2021)
The Amazon Event, Amazon’s Play for Neighborhoods, Amazon Astro. Today’s update will be focused on Amazon’s product event. We kick things off with my thoughts regarding Amazon’s product strategy involving ambient intelligence. The discussion then turns to Ring’s outsized presence throughout Amazon’s presentation. We go over Amazon’s play for neighborhoods and what is at stake. The update concludes with a closer look at the Amazon Astro. (Sep 29, 2021)
Here are the five most popular daily updates published in 2021 based on page views to AboveAvalon.com. There is naturally a tendency for updates published earlier in the year to outrank more recent updates.
Apple Designer Eugene Whang Left Apple, Apple Industrial Design Turnover, Spotify’s WSJ Op-Ed Against Apple (May 19, 2021)
Peloton Acquires Wearables Company, Peloton vs. Apple Watch, Facebook Talks Up Smartwatch as AR Controller (Mar 23, 2021)
Tesla’s Bitcoin Problem, Apple and Bitcoin Mining, Introducing My FY2022 Estimates for Apple (Feb 11, 2021)
Target to Open Mini Apple Stores, Apple’s Retail Store Growth Strategy, Thursday Q&A (Feb 25, 2021)
Apple Contemplating Apple Watch Explorer Model, Thinking About the Apple Watch Line, Apple Watch Partnerships (Mar 29, 2021)
Just 13% of the daily updates published in 2021 are highlighted in this article. The full archive consisting of all 182 daily updates is available here. Above Avalon membership is required to access the updates.
Daily Podcast
This was the first full year for the Above Avalon Daily podcast, the private podcast available to members who attached the podcast add-on to their membership. A total of 182 episodes were published, totaling nearly 40 hours of audio. The podcast allows members to consume the daily updates in new and different ways while around the house, on a walk, or in the car. Since launch, reception of the daily podcast has exceeded my expectations with very positive listener feedback. More information on the daily podcast, including a few sample episodes, is found here. Once an Above Avalon member signs up for the daily podcast, all prior episodes become available for listening in podcast players that support private podcasts.
Inside Orchard (Launched in 2021)
In March, I launched InsideOrchard.com as a home to my unique perspective on technology and its impact on society. Over the past nine months, 40 essays and corresponding podcast episodes were published. Although distinct from the analysis and discussion found with Above Avalon, the two sites can be thought of as siblings. A bundle consisting of both an Above Avalon membership and Inside Orchard subscription, with an accompanying price discount, was purchased by a good percentage of the Above Avalon member base.
Here’s to 2022
A big thank you goes out to readers, listeners, and members for making 2021 another successful year for Above Avalon. Have a safe and relaxing Christmas, holiday season, and New Year. See you in 2022. - Neil
The Above Avalon Daily Update Recap (3Q21 Edition)
I publish exclusive daily updates all about Apple throughout the week. The updates contain my perspective and analysis on Apple’s business, product and financial strategy, and competitive relationships with a range of companies. The updates have become widely read and influential in the world of Apple and tech and are ideally suited to executives, investors, project managers, and hobbyists. When combined with the periodic articles and podcast episodes, which are accessible to everyone, the updates provide the full Above Avalon experience throughout the week.
During the third quarter of 2021 (July to September), 48 Above Avalon daily updates were published, chronicling both noteworthy industry and Apple-specific stories as well as my Apple research. The major themes discussed during the quarter included:
Developments in the App Store regulatory space (South Korea, Japan, Epic Games Vs. Apple trial).
Apple TV / paid video streaming industry developments.
Apple unveiling its Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) detection plan and the resulting fallout.
Project Titan leadership changes and developments in the EV space.
The Above Avalon Daily Update Recap (3Q21 Edition) goes over these major themes and the corresponding daily updates.
(To access the following updates, become a member and then request access to the daily updates archive found in Slack.)
Developments in the App Store Regulatory Space (South Korea, Japan, Epic Games Vs. Apple trial)
After years of discussion and debate regarding Apple’s handling of the App Store, there was notable movement on the App Store legal and regulatory fronts. During 3Q, Apple notched two App Store victories in U.S. courts, South Korea rushed an anti-App Store bill through, and Apple began to loosen its grip on some of the more controversial App Store guidelines.
Apple Settles Class-Action Suit from U.S. Developers, Why Settle Now?, The iOS Developer Divide (Aug 30, 2021)
Thoughts on the Epic Games vs. Apple Ruling (Sep 13, 2021)
Peloton Earnings, South Korea Passes App Store Payments Bill, Apple Acquires Primephonic (Aug 31, 2021)
Sonos 3Q21 Earnings, Anti-App Store Legislation Introduced in Senate, The Bill’s Privacy and Security Exemption (Aug 12, 2021)
Apple TV / Paid Video Streaming Industry Developments
The paid video streaming industry continues to intrigue as it expands and evolves. There were a number of noteworthy events and developments during 3Q including Netflix’s move into gaming, a “Ted Lasso” bonanza, and the Netflix vs. Disney dynamic. I also went over my estimate for the number of Apple TV+ subscribers.
Netflix Moving Forward with Gaming, Entertainment Bundles Will Win, This Time Is Different for Games (Jul 15, 2021)
Netflix 2Q21 Earnings, Netflix Is Feeling Competitive Pressure, Netflix’s Video Gaming Strategy (Jul 21, 2021)
Apple’s Return to the Office Brouhaha, Apple Searching for Hollywood Hub, The Ted Lasso Effect (Jul 20, 2021)
Disney Earnings, Disney Will Surpass Netflix, Roku Earnings (Aug 23, 2021)
EU’s Vestager Threatens Apple, Video Streaming Box Market Shares, Peacock Signs Universal Deal (Jul 7, 2021)
Apple and the NFL, Disney’s Black Widow Opening Weekend, A Laptop Revival (Jul 12, 2021)
The Apple TV Debate Rages On, Apple’s Home Strategy, Smart Homes and Ecosystems (Aug 11, 2021)
Apple Unveiling Its Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) Detection Plan and the Resulting Fallout
In August, Apple lit a firestorm of a debate by announcing a plan to combat child sexual abuse. The plan ended up drawing into question a number of philosophical questions as to Apple’s role in society and the company’s reason for being.
Apple Announces Expanded Protections for Children, Thoughts on Apple’s CSAM Detection, Apple CSAM and the Slippery Slope (Aug 9, 2021)
Apple Head of Privacy Talks CSAM Detection, CSAM Detection FUD, Apple and the Privacy High Ground (Aug 10, 2021)
Apple Releases Security Threat Model Review of CSAM Detection, Apple Doing Damage Control, Genuine Pushback to Apple’s CSAM Detection (Aug 16, 2021)
Project Titan leadership changes
Apple’e electric car project continued to move forward with a major leadership change as Apple Watch software chief Kevin Lynch replaced Doug Field as Titan head.
Doug Field Leaves Apple for Ford, Project Titan’s Trajectory and Leadership, Silicon Valley vs. Detroit (Sep 8, 2021)
Apple’s Kevin Lynch Joins Project Titan, Apple Car Implications, Apple Watch Implications (Jul 19, 2021)
Tesla Earnings, Elon Musk Goes After Apple Again, Musk Steps Away from Earnings Calls (Jul 27, 2021)
Follow the Tech Capex, Apple’s Reliance on Chinese Suppliers Increases, Foxconn Moving Forward With Car Factories in U.S. (Aug 18, 2021)
A few additional updates published between July to September stood out to me.
The Amazon Event, Amazon’s Play for Neighborhoods, Amazon Astro (Sep 29, 2021)
Square Acquires Afterpay, Square vs. Apple, The Future of Credit (Aug 3, 2021)
Apple’s Services Journey, A Different Way of Thinking of Apple One, Apple Services Evolution (Jul 13, 2021)
Above Avalon membership is required to read the preceding daily updates. There are two membership options available: $20/month or $200/year. The annual option amounts to a $40 discount. Payment is hosted and secured by MoonClerk and Stripe. Apple Pay is accepted. You can update your payment information and membership status at any time on this page.
Above Avalon Podcast Episode 181: Let's Talk Apple Retail
When asked to identify Apple’s crown jewel, most will point to the iPhone or iPad. Apple’s retail operations probably wouldn’t be too high on many people’s lists. This is a mistake. In episode 181, Neil discusses Apple’s retail operations with a focus on where Apple Retail is headed and what changes are needed. Discussion topics include the three distinct phases that Apple Retail has experienced, the roles that Apple stores need to play going forward, and the three big bets that Apple is placing with its stores.
To listen to episode 181, go here.
The complete Above Avalon podcast episode archive is available here.
Subscribe to receive future Above Avalon podcast episodes:
RSS Feed (for your favorite podcast player)
The Above Avalon Daily Update Recap (January 2021)
Along with publishing periodic articles that are accessible to everyone, I publish daily updates all about Apple. These updates are 2,000-word emails that revolve around Apple business and strategy analysis, my perspective and observations on current news and Apple competitors, and comprehensive coverage of Apple earnings, product events, and keynotes. These daily updates have become widely read and influential in the tech sector and Apple universe. The updates are now also available in podcast form called Above Avalon Daily.
Since 90% to 95% of my time is dedicated to researching and writing the daily updates and recording the corresponding daily podcast, I am introducing a new Above Avalon product called The Above Avalon Daily Update Recap to make it easy for everyone to keep abreast of where my focus has been. Each curated recap of the prior month’s updates includes access to one story from a daily update that I particularly enjoyed writing in the previous month.
The daily updates are available exclusive to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
The following story was featured in the Above Avalon Daily Update published on January 14th, 2021 (prior to Apple reporting 1Q21 earnings).
Projections for Apple’s Buyback Pace
Apple has $79B of net cash on the balance sheet. By funding share repurchases and cash dividends, Apple has been gradually chipping away at that total (was $153B in FY17).
Based on my projections, Apple will be able to sustain the current pace of share buyback (approximately $70B per year) for an additional 11 to 13 quarters before net cash gets close to zero.
Where does my 11 to 13 quarters estimate come from?
There is a $25B delta between the amount of cash Apple is returning to shareholders each year ($90B) and annual free cash flow ($65B) - the amount of cash generation leftover after management has paid all of the bills and maintained / funded capital investments. Free cash flow is used to manage debt in addition to fund cash dividends and share repurchases. Meanwhile, Apple has $79B of net cash on the balance sheet. ($79B / $25B = 3.2 years or 13 quarters).
It is important to note that these are rough calculations. Apple’s cash needs will fluctuate year to year. This will have an impact on Apple's free cash flow. In addition, it would not be essential to know the exact moment net cash neutral is obtained, if Apple ever technically gets to that level, but rather when net cash is in the vicinity of $0.
Once Apple reaches a net cash neutral position, my estimate is Apple’s buyback pace will slow to something closer to $50B per year. This total is primarily derived from my Apple free cash flow projection ($70B per year) minus cash dividend expense ($15B per year). Over time, Apple's buyback pace can certainly increase to remain in line with free cash flow growth. The reverse is true as well - a slowdown in free cash flow may result in less buyback.
These estimates assume that Apple management continues to view share buyback as attractive at the current share price. That decision will ultimately be based on management's estimate of Apple's intrinsic value. Based on Apple's most recent buyback activity, management thinks Apple's intrinsic value is higher than $115 per share.
In January, a total of 15 daily updates containing 45 stories were published. Those 45 stories have been rearranged into the following categories:
Earnings / Financials
My Apple 1Q21 Estimates, Wall Street’s Expectations, The Apple Number to Watch (My Apple 1Q21 earnings preview)
Apple Earnings, The Most Important Apple Number, Apple Remains Misunderstood (My Apple 1Q21 earnings review)
Product Strategy
Business Strategy
Management / Leadership
Apple Peers and Competitors
Industry Analysis
Thursday Q&A (The following questions were submitted by Above Avalon members.)
Doesn’t Peloton make more sense as a health acquisition target for Google than Fitbit?
Are you still expecting double-digit iPhone unit sales growth in 2021?
What do you make of the rumors that Apple will remove the Touch Bar from new MacBook Pros?
What do you make of IDC and Gartner projecting huge growth numbers for Mac over the holidays?
All of the following stories are accessible to members via the Daily Updates archive. Access to the archive is a benefit attached to membership. For new members, information about accessing the archive will be sent to you after going through the signup process.
The daily updates are also available via a private podcast called Above Avalon Daily. In January, 14 podcast episodes were recorded for a total of 200 minutes of audio. The daily podcast is available as an add-on that can be attached to an Above Avalon membership. More information on the podcast is available here. All prior episodes will appear in your podcast player after you sign up for the Above Avalon Daily podcast.
Above Avalon Year in Review (2020)
Heading into 2020, the big question facing Apple was found with growth. Apple had reached a billion users. Would Apple be able to reach two billion users in the 2020s by continuing to do what it had been doing or would more in the way of strategy shifts be needed?
As it did with every company, the pandemic turned 2020 into a steady stream of unexpected challenges for Apple. The company needed to figure out a way to continue product development on a global scale with little to no employee travel. Apple retail needed to be completely rethought as social distancing initiatives ruled out the usual crowded Apple stores. Apple events (both WWDC and product unveilings) needed to go virtual.
According to my estimate, Apple saw approximately $20 billion of delayed demand in FY2020 as a result of the pandemic. Approximately 15 million iPhone upgrades were delayed while wearables sales faced pressure due to retail stores being closed. Partially offsetting those headwinds, iPad and Mac results have been stellar as consumers upgrade older machines and look for larger displays to support working at home and distance learning.
Articles
In 2020, I published 15 Above Avalon articles. In looking through the articles, which are accessible to all, there was one overarching theme: Apple’s improving competitiveness in comparison to that of its peers and the steps the company is taking to position itself for continued ecosystem growth in the 2020s.
Here are some of my favorite articles published in 2020 (in no particular order):
Apple Is Pulling Away from the Competition. Relying on an obsession with the user experience, Apple is removing oxygen from every market that it plays in. At the same time, the tech landscape is riddled with increasingly bad bets, indifference, and a lack of vision. Apple is pulling away from the competition to a degree that we haven’t ever seen before.
The Secret to Apple's Ecosystem. Apple’s ecosystem remains misunderstood. There is still much unknown as to what makes the ecosystem tick. From what does Apple’s ecosystem derive its power? Why do loyalty and satisfaction rates increase as customers move deeper into the ecosystem? Apple’s ecosystem ends up being about more than just a collection of devices or services. Apple has been quietly building something much larger, and it’s still flying under the radar.
A Billion iPhone Users. A billion people now have iPhones. According to my estimate, Apple surpassed the billion iPhone users milestone last month. Apple’s top priorities for the iPhone include finding ways to keep the device at the center of people’s lives while at the same time recognizing the paradigm shift ushered in by wearables.
Apple’s $460 Billion Stock Buyback. Share buybacks came under fire earlier this year. Some companies that were recent buyers of their shares found themselves in financial distress and seeking bailouts due to economic fallout from the pandemic. A very good argument can be made that Apple has become the poster child of responsible share repurchases. The company has relied on its stellar free cash flow to fund share repurchases over the years.
Apple Watch and a Paradigm Shift in Computing. Despite being only four years old, the Apple Watch has fundamentally changed the way we use technology. Many tech analysts and pundits continue to look at the Apple Watch as nothing more than an iPhone accessory - an extension of the smartphone that will never have the means or capability of being revolutionary. Such a view is misplaced as it ignores how the Apple Watch has already ushered in a paradigm shift in computing.
The five most popular Above Avalon articles in 2020, as measured by page views, were identical to my favorites list.
Podcast Episodes
There were 16 episodes of the Above Avalon podcast recorded and published in 2020, totaling seven hours. The podcast episodes that correspond to my favorite articles are found below:
Charts
The following charts found in Above Avalon articles were among my favorite published in 2020.
Number of Users
While Apple new user growth rates have slowed, the company is still bringing tens of millions of users into the fold. Due to Apple’s views regarding innovation and its focus on the user experience, once someone enters the Apple ecosystem, odds are good that customer will remain in the ecosystem.
Apple Installed Base (Number of Users)
Apple Non-iPhone Revenue Growth
Apple finds itself in an ecosystem expansion phase. Hundreds of millions of people with only one Apple device, an iPhone, are embarking on a search for more Apple experiences. We see this with non-iPhone revenue growing by double digits in the back half of 2020 on a TTM basis, which is higher than growth rates seen in the mid-2010s.
Apple Non-iPhone Revenue Growth Projection
The Apple Innovation Feedback Loop
With Apple Silicon, Apple took lessons learned from personal devices such as Apple Watches, iPhones, and iPads to help push less personal devices, like the Mac, forward.
Daily Updates
In 2020, I published 196 Above Avalon Daily Updates that were available exclusively to Above Avalon members. With each update coming in at approximately 2,000 words, 196 updates are equivalent to seven books. This continues to be an industry-leading number when it comes to the amount of Apple business and strategy analysis published.
When looking over the topics discussed in this year’s daily updates, a few sub themes become apparent:
Apple and the Pandemic
When the pandemic began during the first half of the year, there was much unknown as to how a company like Apple would be impacted. It eventually became clear that Apple and its peers were positioned to do OK during the pandemic although new ways of thinking would be needed to navigate working from home and travel restrictions.
Big Tech Gaining Power in the Pandemic, Apple's Source of Power, Former Apple Industrial Designer Starts Speaker Company (May 28, 2020)
New iPhone Production Starting Soon, iPhone Production Estimates, Apple’s HW Solution for Pandemic Travel Restrictions (Sep 8, 2020)
Apple’s Place in a Stay-at-Home Economy, E-Commerce Acceleration, Some iPad and Mac Production Moving to Vietnam (Nov 30, 2020)
The Paid Video Streaming Battle
With Disney+ and Apple TV+ launching in late 2019 and HBO Max and Peacock launching this past May and July, respectively, 2020 turned out to be the legitimate start of the paid video streaming battle. As the true new kid on the block, Apple learned quite a bit about being more than just a distributor of other people’s content.
Apple Wins Ireland Tax Battle, Apple Hints at Apple TV+ Subscriber Total, Apple’s In-House Content Studio (Jul 15, 2020)
Thoughts on Early iPhone Sales, Disney Reorganizes, Disney Is Streaming’s New Poster Child (Oct 19, 2020)
A Video Content Distribution War, Roku and Amazon vs. Peacock and HBO Max, Microsoft Attacks the App Store (Jul 21, 2020)
Apple Sales Mix by Display Size, WarnerMedia’s Huge Movie Announcement, Apple and Movies (Dec 7, 2020)
Pushback Against the App Store
Apple is pulling away from the competition, and the App Store is considered the best (and last) chance for competitors to reshape the mobile industry to their liking. A series of legal and PR battles were waged against the App Store by a handful of smaller app developers and larger Apple competitors.
Tech CEOs Testify in Front of Congress, Congress’s Concern Regarding Apple, Apple’s Trouble Area (Jul 30, 2020)
Epic Games Breaks App Store Guidelines, Epic Games’ Epic Hypocrisy, The App Store’s Future (Aug 17, 2020)
The Coalition for App Fairness, A New Guerrilla Warfare Tactic, The Coalition’s Questionable Website (Sep 29, 2020)
The House Antitrust Report on Big Tech, Massive Holes in the Antitrust Report, Apple’s Response (Oct 8, 2020)
When looking at my daily updates published in 2020, selecting a handful of favorites out of 196 updates was not an easy task. The following updates stood out to me (in no particular order):
Apple’s Organizational Structure, Apple’s Leadership Structure, An Autonomous Apple. We first go over my thoughts on Apple’s functional organizational structure and the difference between a functional and multidivisional structure. The discussion then turns to Apple leadership and the ideas of “discretionary leadership” and “experts leading experts.” The update concludes with a revisiting of my Above Avalon article, “Jony Ive, Jeff Williams, and a Larger Apple” and a discussion of how Apple has been able to become a larger design company. (Oct 26, 2020)
Nike Earnings, The Similarity Between Nike and Apple, A Stronger Apple and Nike Partnership. We kick off this update with my thoughts on Nike’s earnings. After going over three structural tailwinds facing Nike, we discuss why I think Nike is pulling away from the competition. The discussion then turns to how Nike is the company most like Apple. The update concludes with a look at how Apple and Nike are both interested in health. We go over the competitive dynamic between the two companies and why it’s premature to conclude that Apple and Nike will become fierce competitors in the future. (Sept 24, 2020)
iPhone Momentum Building in Europe, Apple's Good Timing with iPhone SE, Selling Utility on the Wrist. We begin this update with my thoughts on the iPhone gaining momentum in Europe. The discussion includes new iPhone sales share data and what looks to be some kind of inflection point in the region. We also discuss the possible factors behind the inflection point. The update then turns to how Apple ended up launching the updated iPhone SE at just the right time. We then take a closer look at wearables competition on the wrist. In particular, we go over Fitbit’s latest earnings and compare fitness tracker and smartwatch demand. The discussion concludes with why Amazon Halo faces an uphill battle for wrist real estate. (Sep 3, 2020)
Valuing Big Tech on Free Cash Flow, AAPL vs. Free Cash Flow, AAPL vs. Low Interest Rates. This update begins with my thoughts on the idea that Wall Street has changed the way it is valuing Apple - one away from focusing on P/E ratios (price-to-earnings) and more towards free cash flow valuation. After going over the free cash flow yields for the tech giants, we look specifically at Apple’s declining free cash flow yield and what it tells us about how the market is approaching the company. The update concludes with a discussion of interest rates, inflation, and the U.S. Fed looking to embrace elevated inflation before seeing the need for higher rates. There are various AAPL-related implications associated with that development. (Aug 25, 2020)
Apple Acquires NextVR, Apple Glasses in 2022?, A Wearables Platform for the Face. We begin this update with my thoughts on Apple acquiring NextVR. The discussion includes the reasons why I think Apple acquired NextVR and how the company can play a role in Apple’s product strategy. The update then turns to new rumors about Apple Glasses launch dates. Simply put, the Apple AR / VR rumor mill is getting out of hand. We go over two factors that I think are driving the varied rumors regarding Apple Glasses. The discussion concludes with a different way of thinking about AR / VR and Apple. (May 18, 2020)
Warren Buffett’s Annual Letter, The Power of Apple Retained Earnings, Imploding Demand for Fitbit. We kick off this update by examining Warren Buffett’s annual letter to Berkshire Hathaway shareholders. Berkshire Hathaway is Apple’s largest individual shareholder. Accordingly, there is value in keeping on top of Berkshire and Warren Buffett (Berkshire’s CEO and Chairman of the Board). The discussion then turns to retained earnings and why Apple’s retained earnings are such a powerful tool. We conclude with a look at Fitbit’s awful 4Q19 earnings and why the company represents such a problem for Google. (Feb 24, 2020)
Here are the five most popular daily updates published in 2020 based on page views:
iPhone Sales Share Rises During Pandemic, It’s All About Smartphone Upgrading, A $5,000 Swiss Smartwatch (Jun 3, 2020)
Google Pixel Shakeup, Consumer Spending During the Pandemic, Surface Sales vs. iPad and Mac Sales (May 14, 2020)
Apple vs. Hey (Jun 17, 2020)
The App Store’s Impact on Apple Financials, Facebook Launches Paid Online Events, 4Q20 Microsoft Surface Results (Aug 18, 2020)
Just 11% of the daily updates published in 2020 are highlighted above. The full archive consisting of all 196 daily updates is available here. Membership is required to access the updates.
Daily Podcast (Launched in 2020)
In 2020, Above Avalon Daily Updates became available in audio for the first time via a private podcast called Above Avalon Daily. Reception to the daily podcast continues to exceed my expectations with very positive listener feedback. The podcast has allowed members to consume the daily updates in new and different ways while around the house, on a walk, or in the car. More information on the daily podcast, including a few sample episodes, is found here. Above Avalon Daily was launched in August, and 66 episodes were published in 2020, totaling nearly 17 hours of audio. Once a member signs up for the daily podcast, all prior episodes become available for listening in podcast players that support private podcasts.
Here’s to 2021
Without question, 2020 ended up being the busiest year for Apple since Above Avalon was launched in 2014. There was no shortage of newsworthy stories, and all indicators point to the fast pace continuing into 2021. A big thank you goes out to Above Avalon readers, listeners, and members for making 2020 another successful year for Above Avalon.
Apple Watch Momentum Is Building
In a few months, the number of people wearing an Apple Watch will surpass 100 million. While the tech press spent years infatuated with stationary smart speakers and the idea of voice-only interfaces, it was the Apple Watch and utility on the wrist that ushered in a new paradigm shift in computing. We are now seeing Apple leverage the growing number of Apple Watch wearers to build a formidable health platform. The Apple Watch is a runaway train with no company in a position to slow it down.
Mirages and Head Fakes
We are coming off of a weird stretch for the tech industry. As smartphone sales growth slowed in the mid-2010s, companies, analysts, and pundits began to search for the next big thing. The search landed on stationary smart speakers and voice interfaces.
Companies who weren’t able to leverage the smartphone revolution with their own hardware placed massive bets on digital voice assistants that would supposedly usher in the end of the smartphone era. These digital voice assistants would be delivered to consumers via cheap stationary speakers placed in the home. Massive PR campaigns were launched that attempted to convince people about this post-smartphone future. Unfortunately for these companies, glowing press coverage cannot hide a product category’s fundamental design shortcomings.
At nearly every turn, Apple was said to be missing the voice train because of a dependency on iPhone revenue. Management was said to suffer from tunnel vision while the company’s approach to privacy was positioned as a long-term headwind that would lead to inferior results in AI relative to the competition. Simply put, Apple was viewed as losing control of where technology was headed following the mobile revolution.
There were glaring signs that narratives surrounding smart speakers and Apple lacking a coherent strategy for the future were off the mark. In November 2017, I wrote the following in an article titled, “A Stationary Smart Speaker Mirage”:
“On the surface, Amazon Echo sales point to a burgeoning product category. A 15M+ annual sales pace for a product category that is only three years old is quite the accomplishment. This has led to prognostications of stationary smart speakers representing a new paradigm in technology. However, relying too much on Echo sales will lead to incomplete or faulty conclusions. The image portrayed by Echo sales isn't what it seems. In fact, it is only a matter of time before it becomes clear the stationary home speaker is shaping up to be one of the largest head fakes in tech. We are already starting to see early signs of disappointment begin to appear…
I don’t think stationary smart speakers represent the future of computing. Instead, companies are using smart speakers to take advantage of an awkward phase of technology in which there doesn’t seem to be any clear direction as to where things are headed. Consumers are buying cheap smart speakers powered by digital voice assistants without having any strong convictions regarding how such voice assistants should or can be used. The major takeaway from customer surveys regarding smart speaker usage is that there isn’t any clear trend. If anything, smart speakers are being used for rudimentary tasks that can just as easily be done with digital voice assistants found on smartwatches or smartphones. This environment paints a very different picture of the current health of the smart speaker market. The narrative in the press is simply too rosy and optimistic.
Ultimately, smart speakers end up competing with a seemingly unlikely product category: wearables.”
Three years later, I wouldn’t change one thing found in the preceding three paragraphs. The smart speaker bubble popped less than 12 months after publishing that article. The product category no longer has a buzz factor, and despite the hopes of Amazon and Google, people are not using stationary speakers for much else besides listening to music and rudimentary tasks like setting kitchen timers.
The primary problem found with voice is that it’s not a great medium for transferring a lot of data, information, and context. As a result, companies like Amazon have needed to dial back their grandiose vision for voice-first and voice-only paradigms. Last week’s Amazon hardware event highlighted a growing bet on screens – a complete reversal from the second half of the 2010s.
Betting on the Wrist
As companies who missed the smartphone boat were placing bets on stationary speakers, Apple was placing a dramatically different bet on a small device with a screen. This device wouldn’t be stationary but instead push the definition of mobile by being worn on the wrist.
Jony Ive, who is credited with leading Apple’s push into wrist wearables, referred to the wrist as “the obvious and right place” for a different kind of computer.
When Apple unveiled the Apple Watch in 2014, wearable computing on the wrist was more of a promise than anything else. Apple created an entirely new industry – something that isn’t found much in the traditional Apple playbook.
After years of deep skepticism and cynicism, consensus reaction towards Apple Watch has changed and is now positive. Much of this is due to the fact that it’s impossible to miss Apple Watches appearing on wrists around the world. According to my estimates, approximately 35% of iPhone users in the U.S. now wear an Apple Watch. This is a shockingly high percentage for a five-year-old product category, and it says a lot about how Apple’s intuition about the wrist was right.
Apple Watch Installed Base
The number of people wearing an Apple Watch continues to steadily increase. According to my estimate, there were 81 million people wearing an Apple Watch as of the end of June. According to Apple, 75% of Apple Watch sales are going to first-time customers. This means that 23 million people will have bought their first Apple Watch in 2020. To put that number in context, there are about 25 million people wearing a Fitbit. The Apple Watch installed base is increasing by the size of Fitbit’s overall installed base every 12 months. Exhibit 1 highlights the change in the Apple Watch installed base over the years.
Exhibit 1: Apple Watch Installed Base (number of people wearing an Apple Watch)
(The calculations and methodology used to reach my Apple Watch installed base estimates is available here for Above Avalon members.)
Deriving Power
From where is Apple Watch deriving its momentum? The answer is found in The Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products.
One of the core tenets of my theory is that an Apple product category's design is tied to the role it is meant to play relative to other Apple products. The Apple Watch is designed to handle a growing number of tasks once given to the iPhone. Meanwhile, the iPhone is designed to handle a growing number of tasks given to the iPad. One can continue this exercise to cover all of Apple's major product categories.
Apple Watch is not an iPhone replacement because there are things done on an iPhone that can't be done on an Apple Watch. This ends up being a feature, not a bug. The Apple Watch’s design then allows the product to handle entirely new tasks that can’t be handled on an iPhone. This latter attribute goes a long way in explaining how Apple Watch has helped usher in a new paradigm shift in computing. Apple Watch wearers are able to interact with technology differently.
(More on The Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products is found in the Above Avalon Report, “Product Vision: How Apple Thinks About the World,” available here for Above Avalon members.)
A Health Platform
In January 2019, Tim Cook surprised many by saying Apple will be remembered more for its contributions to health than for any other reason. Here’s Cook:
“I believe, if you zoom out into the future, and you look back, and you ask the question, ‘What was Apple’s greatest contribution to mankind?’ it will be about health.”
Many assumed that Cook’s comment hinted at Apple unveiling a portfolio of medical-grade devices that would go through the FDA approval process. Such thinking was based on a fundamental misunderstanding of Apple’s ambition and approach to product development.
Apple’s health strategy is based on leveraging hardware, software, and services to rethink the way we approach health. This means Apple wasn’t going to just launch a depository for our health data – something that is needed but which ultimately falls short of being truly revolutionary. In addition, Apple wasn’t going to just offer health and fitness services that amount to counting steps or keeping track of miles run.
By the time Cook gave his bullish comment about health, Apple had already placed its big bet on health four years earlier by unveiling the Apple Watch. In what ended up being one of Apple’s best decisions, the company avoided going the route of medical-grade devices requiring government agency approval to reach consumers. Instead, Apple framed its health platform as a new-age computer that ultimately is an iPhone alternative.
Health monitoring is one of the key new tasks that the Apple Watch, not iPhone, handles. To be more precise, Apple Watch is handling the following four health-related items:
Proactive monitoring (i.e. heart rate and blood oxygen)
Well-being assistance (i.e. sleep monitoring including the runup to sleep)
Fitness and activity tracking (i.e. Activity and Workout apps)
Fitness and health activity (i.e. Apple Fitness+)
With Apple Fitness+, Apple didn’t just release a virtual fitness class service. Instead, Apple Fitness+ is an Apple Watch service. In some ways, Apple Fitness+ reminds me of Apple TV+. A future in which Fitness+ workouts are available on third-party gym equipment displays including on treadmills and stationary bikes is not a stretch. In addition, classes from other companies such as Nike could further elevate Apple Fitness+.
Competition
If the Apple Watch is a runaway train, there is no obvious candidate in a position to stop or even slow the train. While other companies are slowly waking up and seeing the momentum found with Apple Watch, there is still much indifference, mystery, and misunderstanding as to why people are buying wearables. Too many companies still think of wearables as glorified smartphone accessories. Such thinking makes it impossible for competitors to see how Apple Watch is ushering in a paradigm shift in computing by making technology more personal in a way that other devices have failed to accomplish or replicate.
One of the main takeaways from Apple’s product event earlier this month is how Apple is its own toughest competitor. The Apple Watch’s most legitimate competition is found with older Apple Watches and non-consumption (i.e. empty wrists). While this introduces its own set of risks and challenges, there is still no genuine Apple Watch competition from other companies after six years. This is an indication of the power found in controlling your own hardware, software, and services in order to get more out of technology without having technology take over people’s lives.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members in both written and audio forms. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
For additional discussion on this topic, check out the Above Avalon daily update from October 1st.
Attacking the App Store
Apple competitors have turned to guerrilla warfare tactics to wage a battle against Apple and the App Store. Based on what is being written and said about the App Store, one would think we have an entered a tech dystopia in which 27 million iOS developers and a billion Apple users are being taken advantage of by Tim Cook and his allegiance to Wall Street.
What had been valid criticism aimed at the App Store has descended into calls to burn everything down and replace it with anti-consumer and anti-developer alternatives. The writing is on the wall. Apple is pulling away from the competition, and the App Store is considered the best (and last) chance for competitors to reshape the mobile industry to their liking.
App Store
We have never seen anything like the App Store, a curated marketplace where a billion users can access 1.7 million apps. Apple established an easy, safe, private, and convenient way for consumers to personalize nearly 1.3 billion iPhones and iPads with third-party applications. Approximately 500 million people visit the App Store each week - a remarkable figure that speaks to how the App Store continues to connect with consumers on a global basis. In FY2019, App Store revenue was an estimated $53 billion. Apple’s share of that revenue came out to an estimated $14 billion. (Apple generates much less when it comes to App Store profit.)
Some have tried to say that there was a viable, safe, cost efficient, and overall compelling form of software distribution to the mass market prior to the existence of the App Store. There’s one problem with such a claim: The mass market didn’t consume software prior to the App Store. In 2008, the year the App Store launched, only 20% of people even had access to the internet.
There are a number of reasons why the iPhone installed base is eight times larger than the Mac installed base, and the App Store is high on the list.
Evolving Criticism
The App Store is not perfect. A small, but vocal, segment of the iOS developer community (now 27 million strong) has spent years raising concerns and issues regarding the App Store, and in particular, app review and the way Apple enforces App Store guidelines.
However, over the past 18 months, App Store criticism began to take on a dramatically different look and feel as multi-nationals entered the fray. In just the past few months, Facebook, Microsoft, Airbnb, and Epic Games have raised concerns about the App Store.
Spotify was one of the early App Store opponents. The company took what now looks like a delicate approach to raising specific issues with the App Store and what it deemed to be anticompetitive behavior on Apple’s part. While the company was grasping at straws with most of its claims, a few concerns had merit.
Microsoft decided to go behind Apple’s back to secretly get U.S. lawmakers to investigate the App Store on monopolistic grounds. Airbnb ran to the New York Times to air its grievance about wanting a special deal from Apple so it didn’t need to follow long-standing App Store guidelines.
However, it was Epic Games’ attack against Apple that marked a turning point in App Store criticism. Epic relied on a different kind of strategy:
Breaking App Store guidelines willingly and blatantly. We have never seen a company actually take pride in breaking App Store guidelines. Epic made sure everyone knew it was breaking App Store rules by offering a virtual currency as an in-app purchase without going through Apple payment.
Leveraging users and press to its advantage. Instead of making the battle be between two companies, Epic weaponized its user and fan base in an attempt to wage an uprising against Apple. In this pursuit, Epic also tried to use the press more than any other company that came before it in going after the App Store.
These corporations are ultimately after the same goal – to weaken Apple’s ironclad grip over the App Store. While many independent developers are simply focused on finding financial sustainability for their families, the multi-nationals are more interested in pulling iOS from under Apple’s control in order to gain power at the expense of Apple.
Why the App Store?
Apple is pulling away from the competition like never before. A revised product strategy (pull to push), and a broader consumer technology landscape that is swinging and missing on bet after bet, are the two primary factors behind Apple’s momentum. However, the App Store plays a vital role in setting Apple devices apart from the competition.
Accordingly, the App Store may seem like an unusual target for Apple competitors. The digital storefront is very popular with users (based on usage trends) and developers. (Most developers don’t pay Apple anything beyond a nominal developer fee to transact business through the App Store.)
No one is questioning the App Store’s success or popularity. Instead, competitors see a way to turn that success into a weakness. Due to extensive lobbying efforts, most of which were driven by Apple competitors, governments and regulatory bodies from around the world are investigating the claim that Apple is relying on monopolistic behavior to achieve App Store success.
Competitors see these regulatory investigations as a potential vulnerability in Apple’s armor. Breaking up or watering down the App Store would allow competitors to leverage the iOS ecosystem to their advantage. In essence, Apple would lose control over app distribution in its own ecosystem. Competitors would no longer be subject to revenue share arrangements with Apple. In addition, they would be able to establish their own digital storefronts to go direct to customers.
Guerrilla Warfare
Companies like Epic don't want there to be a genuine debate about the App Store. If the debate were to boil down to one’s experience using the App Store, Epic and other App Store critics would lose.
However, the goal is to change the narrative and position the App Store as being fundamentally broken with the only remedy being alternative app stores free from Apple oversight. This sentiment is summarized in the following tweet from Epic Games founder and CEO Tim Sweeney:
“At the most basic level, we’re fighting for the freedom of people who bought smartphones to install apps from sources of their choosing, the freedom for creators of apps to distribute them as they choose, and the freedom of both groups to do business directly.”
We are witnessing a guerrilla war that is being waged by Apple’s competitors. This campaign includes companies and CEOs trying to win the moral high ground by appealing to consumers’ and developers’ emotions. Other goals include trying to distract and tire Apple with relentless App Store attacks coming from all directions and using the press to do much of the heavy anti-App Store lifting.
Nearly every article written about Apple’s latest App Store controversy and battle inevitably includes paragraphs of boilerplate language regarding the App Store’s growing list of regulatory issues around the world. Meanwhile, no space is dedicated to the holes and hypocrisy found in competitors’ claims and allegations against the App Store. This is a classic example of a PR guerrilla warfare tactic utilized by competitors in an attempt to sway the discussion and public opinion.
There are then companies running to the press to paint Apple as the evil behemoth going after small business owners during the pandemic. Facebook, Airbnb, and ClassPass have relied on such shady tactics to attack Apple. Portraying Apple as a small business killer is a new low.
True Intentions
To a certain extent, companies like Epic have been successful in quelling App Store debate. Allegations that Apple is milking developers in order to drive revenue and profit growth are passed around with no supporting evidence or numbers. (My financial estimates for App Store profitability on both a net and gross basis are found here.) Pointing out that the App Store isn’t as profitable as consensus assumes is now met with backlash. None of this was the case just 12 months ago.
The lack of perspective coming from customers is also glaring. Consumers, not Apple, are the group who ultimately ends up supporting tens of millions of developers financially. However, most of the commentary written about the App Store has come from the perspective of competitors with pending lawsuits against Apple.
Hijacking what had been a genuine debate regarding the App Store’s treatment of independent developers in order to prop up their own ambition, companies like Epic are revealing their true intentions. These companies aren’t going after the App Store with the interest of independent developers or users in mind. Advocating for an alternative app store is not pro-developer or pro-consumer. Instead, it’s just a way for these companies to make more money.
Monopolies
At the heart of Epic’s fight against the App Store is the need to have both developers and users on its side. There is a simple reason for such a goal. Epic’s underlying arguments against Apple regarding antitrust are fundamentally weak.
In a 62-page lawsuit filed against Apple, Epic alleges the company holds a monopoly in iOS app distribution and iOS in-app payment processing. There is one problem with such claims: Apple doesn’t have monopolies in any particular product device category. Meanwhile, claiming Apple has a monopoly on what goes on in the App Store is equivalent to claiming Apple has a monopoly on a premium experience.
In what is an ironic twist, Epic ends up demonstrating Apple’s lack of a monopoly in mobile gaming and app distribution. According to Epic, two-thirds of Fortnite users play the game on non-Apple hardware. If Apple held a monopoly on mobile app distribution, Apple’s decision to remove Fortnite from the App Store would have been a lights out moment for the game. Gamers have alternatives if they want to use them.
Need for Debate
It’s time for these guerrilla warfare tactics against the App Store to be called out in an effort to have a genuine debate about the App Store. Such a debate is sorely needed. It wouldn’t be about revenue share percentages, alternative app stores, or items like sideloading. Instead, the discussion is found with how Apple should balance customer and developer interests.
Some iOS developers feel like Apple is treating them like second-class citizens in its ecosystem. These developers want to know why Apple doesn’t go out of its way to make sure they are making as much money as possible. Instead, they feel they are being constantly attacked by App Store review. It’s a valid concern that Apple needs to take seriously.
Are we seeing Apple erring more on the side of customers to the determinant of developers? It may be an uncomfortable question to ask within Apple, but it deserves to be investigated.
Apple positions its customers, not profit, as the guiding light for everything it does. This customer-first focus extends to the App Store as well. Management’s actions with the App Store can be traced to ensuring the store’s viability and vitality. Both are critical for maintaining the App Store as a benefit for consumers. If users are content and happy, developers end up benefitting as well. The two go hand in hand.
There are three things that can help keep the customer versus developer dynamic found with the App Store in proper balance:
1) Allow increased in-app communication between developers and customers. Letting developers communicate more freely with users in apps stands to be a positive development for both parties. Allowing developers to include language like “visit our website for additional ways of buying our service” wouldn’t hurt customers and would be viewed positively for developers. Odds are good that we will see Apple make some changes on this front given the European Commission’s review of App Store practices.
2) Give developers more say over App Store guideline enforcement. App Store guidelines can be thought of as laws with no direct mechanism (like voting) for getting revised or rewritten. The ability to bring cases before some kind of review panel would be a step in the right direction. If there were something like the Supreme Court for App Store guidelines, a panel of Apple executives could determine if certain App Store guidelines would end up harming the broader ecosystem. Last month, Apple announced something along this lines.
3) Come up with the next App Store. By spending time now coming up with tomorrow’s App Store, Apple can benefit both developers and customers. The lack of attention given to this topic is telling. While Apple competitors are eager to replace the App Store with their own mobile app stores, the entire app dynamic loses its relevancy when thinking about wearables. We are going to need a complete rethink of apps as we proceed further into the wearables era.
Dragged Through the Mud
It’s difficult to envision any other product or feature other than the App Store that has done more in bringing such a wide variety of innovation to a billion users. It’s not an understatement to say that the App Store changed the world and is still doing so today.
By painting Apple as a monopolistic giant relying on App Store “tolls” and “taxes” to surpass a two trillion dollar market cap, competitors are dragging the App Store through the mud. Revenue share percentages and angst over App Store guidelines end up being distractions for what is ultimately a classic case of wanting more power. With Apple pulling away from the competition like never before, it’s not a mystery as to why competitors see urgency.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members in both written and audio forms. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
Introducing the Above Avalon Daily Podcast
Over the past five years, 2,000-word written daily updates have served as the cornerstone of Above Avalon membership. With more than 1,000 updates published to date (the archive is found here), the emails have become widely read and influential in the world of Apple.
In an effort to make it easier to consume the daily updates in new and different ways, I am excited to announce a new daily podcast called Above Avalon Daily.
Designed as an add-on feature that can be attached to an existing membership, Above Avalon Daily allows written daily updates to be accessible beyond screens. Members now have the ability to consume the daily updates around the house, on a walk, or in the car.
Podcasting
I am a big believer in podcasts as demonstrated with 172 episodes and counting of the Above Avalon podcast produced over the past six years. Not only does the podcast medium offer a different consumption experience compared to written content, but the two supplement each other. Based on feedback over the years, many AboveAvalon.com readers also listen to the Above Avalon podcast and vice versa. My expectation is that this dynamic will now be found with written and audio versions of the Above Avalon daily updates.
Some may want to listen to Above Avalon Daily first and then read the episode’s “transcript” via the corresponding written daily update. This is especially true for various financial topics covered in the updates. Others will want to read the updates first and then listen to the updates at a later time while driving, at the gym, or doing anything that may limit screen access.
Episode Details
Above Avalon Daily episodes closely follow that day’s written update. Episodes revolve around the following topics:
Apple business and strategy analysis.
My perspective and observations on current news and Apple competitors.
My Apple financial estimates.
Full coverage of Apple earnings, product events, and keynotes.
It became clear early on when creating Above Avalon Daily that one cannot simply take the written daily updates and recite or dictate them word for word. There are too many quoted passages, numbers, exhibits, charts, and data points. Accordingly, each episode includes some curation, new transitions, and commentary that help convert written daily updates into an enjoyable audio format.
Two sample episodes are found below:
Each episode is approximately 15 minutes. Earnings and event episodes will run longer. As with the written daily update schedule, there are four new podcast episodes a week, which works out to a little under 200 episodes a year.
New episodes are released after that day’s daily update is published. Since I am based in the Eastern time zone, new episodes are published in the evening time frame. This makes it possible for new episodes to be listened to first thing the following morning in most regions. New episodes will come out in the AM in Asia and Australia as well. Of course, you can listen to new episodes as soon as they are published.
How to Listen
Transistor is handling the behind-the-scenes mechanics of Above Avalon Daily, a private podcast that can be listened to with various podcast players including Apple Podcasts and Overcast (both of which work great with Above Avalon Daily).
Above Avalon Daily relies on private RSS feeds. This makes it possible for new Above Avalon Daily episodes to show up only for members who have purchased the podcast add-on.
The set-up process for listening to Above Avalon Daily is very simple:
Upon purchasing the podcast add-on, you will receive an email (from “Neil Cybart via Transistor”) that directs you to a sign-up page listing various podcast players that can be used to listen to the podcast. Open the page on an iPhone, and you will see various iOS podcast players. Open the page on a Mac, and you will see options for listening to the podcast on a Mac. A screenshot of that page is found below.
After you select your preferred podcast player, previously-published Above Avalon Daily episodes will automatically appear in your podcast feed. There are already three hours worth of daily updates available. New episodes will appear as they are published.
That’s it. There is no need to create a separate login, password, or Transistor profile. In the vast majority of cases, there is no need to even copy or paste a link or RSS feed.
Pricing and Signing Up
The Above Avalon Daily podcast is available as an add-on ($10 per month or $100 per year) that is attached to an Above Avalon membership.
If you are currently an Above Avalon member, fill out this form to get the podcast add-on. To become an Above Avalon member and purchase the podcast add-on at signup, use the following forms:
Payment is hosted and secured by MoonClerk and Stripe. Apple Pay is accepted. You will receive a confirmation email that includes a link allowing you to update your payment information and membership status at any time.
In addition to being the first podcast exclusive for members, Above Avalon Daily marks the start of members being able to customize their membership to better suit their lifestyle and background. To those members who have already become listeners, thank you for your support. To those of you considering Above Avalon Daily, I am confident you will find the podcast a valuable addition to your daily routine.
The Secret to Apple's Ecosystem
Apple’s ecosystem remains misunderstood. While consensus has come around to accepting the sheer size of Apple’s ecosystem (a billion users and nearly 1.6 billion devices), there is still much unknown as to what makes the ecosystem tick. From what does Apple’s ecosystem derive its power? Why do loyalty and satisfaction rates increase as customers move deeper into the ecosystem? Apple’s ecosystem ends up being about more than just a collection of devices or services. Apple has been quietly building something much larger, and it’s still flying under the radar.
Products
No company is able to match Apple in offering a cohesive and strategically forward-looking product line. Computers small and light enough to be worn on the body are sold next to computers so large that built-in handles are required. More impressively, all of these products are designed to work seamlessly together.
The Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products outlines how each of Apple’s major product categories is designed to help make technology more personal - to reduce the barriers that exist between technology and the user.
Products are designed to handle tasks once handled by more powerful siblings. New form factors are then able to handle new tasks in unique and different ways. It is the pursuit of making technology more personal that ends up being responsible for devices like Apple Watch and AirPods. The same dynamic is also paving the way for Apple to eventually sell wearables for the face in the form of smart glasses. (More on The Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products is found in the Above Avalon Report, “Product Vision: How Apple Thinks About the World,” available here for Above Avalon members.)
With 1.6 billion devices in use, it may be natural to conclude that devices are the source of Apple’s ecosystem power. This has led some to position the iPhone as the sun in Apple’s ecosystem with other products being the planets revolving around the sun. However, this is a misread of the role Apple devices are actually playing in the ecosystem. Just because the iPhone is used by more people than any other Apple device, it is incorrect to assume that will always be the case, or more importantly, that other devices are in some way inferior to the iPhone when it comes to handling workflows. There is something much larger at play here than just a billion users enjoying Apple hardware.
Services
With a $55 billion revenue annual run rate and 518 million paid subscriptions across its platforms, there is no longer a debate as to Apple’s ability to succeed with services. However, there is still a lack of consensus as to what role services play in Apple’s ecosystem. Decisions like bringing Apple Music to third-party speakers and the Apple TV app to third-party TV sets have confused many with some going so far as to conclude that Apple’s future is one of a services company.
In such a world, Apple devices lose much of their value to cheap third-party hardware. This school of thought is responsible for claims that Apple gave up selling accessories like the Apple TV box and HomePod because customers can access Apple content distribution services on cheaper non-Apple hardware. It’s difficult to think of a bigger misread of how Apple thinks and operates as a company than to claim that Apple’s future is one of a services company.
There are now others who look at Apple’s financial success with services as a negative - a sign of Apple milking existing users of as much profit as possible. This school of thought positions paid services as a long-term liability to the Apple ecosystem.
A Toolmaker
While consensus credits products (hardware) as the source of Apple’s ecosystem power, services are increasingly viewed as a hidden risk factor that can crack holes in the ecosystem. Neither are true. Nearly a billion people are not using iPhones simply because they enjoy the hardware. Vice-versa, having 518 million paid subscriptions is not a sign of Apple users needing to pay some kind of tax or bounty to remain in Apple’s ecosystem.
From where then does Apple’s ecosystem derive its power? What makes a customer want to move deeper into the Apple ecosystem?
To answer these questions, we need to step back from any one product or service and instead look at Apple as a company. It is still common for people to call Apple by whatever is its best-selling or most popular product at any one time. This also applies to whatever product is responsible for revenue growth. As a result, we hear all too often phrases like Apple is an iPhone company, a services company, or even a wearables company. The problem is that Apple shouldn’t be defined by any one product, but rather the process that led to Apple having an ecosystem of products and services.
Apple is a design company selling tools that can improve people’s lives. These aren’t just any tools either. Instead, Apple is very selective in selling tools that are able to foster experiences that people are willing to pay for - something that has become increasingly rare in the consumer tech space. By having a design-led culture, Apple is able to put the user experience front-and-center during product development.
This experiences mandate ends up being responsible for Apple’s high loyalty and satisfaction rates. The 975 million people with an iPhone aren’t likely to remain iPhone users because of stellar hardware or compelling software powering that hardware. Instead, loyalty is driven by the experiences associated with using an iPhone.
An Experiences Ecosystem
The secret to Apple’s ecosystem is that instead of selling products or services, Apple ends up selling experiences made possible by controlling hardware, software, and services.
Instead of thinking of Apple’s ecosystem in terms of the number of people or devices, a different approach is to consider the number of experiences Apple is offering. This is where Apple’s true ambitions become visible. By using an iPhone, a customer doesn’t just receive one experience per day. Instead, nearly everything that is consumed on the device has the potential of leading to a good (or bad) experience. This is why Apple’s control of hardware, software, and services plays such a crucial role. Apple’s ecosystem likely consists of tens, if not hundreds of billions, of experiences in a single day.
Having an ecosystem of experiences ultimately represents the biggest challenge to Apple competitors. Coming up with an iPhone alternative isn’t good enough for enticing users to jump from the Apple ship. Instead, competitors need to come up with even better experiences than those found in the Apple ecosystem. As a user moves deeper into the Apple ecosystem - in pursuit of additional premium experiences - competitors need to figure out a way of recreating that growing list of experiences. Can it even be done? When looking at the wearables industry, the answer as of today is “no.”
Non-Apple Hardware
One of the most intriguing aspects of Apple’s ecosystem is how nearly half of Apple users still only use just one Apple device: an iPhone. The idea that every Apple user owns a multitude of Apple devices and services is wrong. The implication is that Apple’s billion users own (and use) quite a bit of non-Apple hardware. Today, non-Apple hardware used by iPhone owners include TV sets, cheap stationary speakers, and CarPlay-equipped automobiles.
Since Apple’s product strategy and organizational structure rewards saying “no” more than “yes,” there will likely always be opportunities for other companies selling hardware to participate in the Apple ecosystem. This ends up being a Trojan Horse for Apple.
Instead of needing to have a new customer jump with both feet into the Apple ecosystem from Day 1, something that isn’t likely especially as the next marginal customer will be coming from the middle tier of the market, Apple merely needs this customer to buy or use one Apple tool.
Management is confident that one tool will eventually turn into two tools and then three since humans gravitate toward premium experiences. As one’s Apple tool collection grows, the number of experiences made possible by those tools increases. This has the impact of increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. And the flywheel continues to turn. In order to get this flywheel moving in the first place, Apple must build bridges allowing new customers to move deeper into the ecosystem. Decisions like making Apple Music available on non-Apple hardware and bringing the Apple TV app to Samsung TVs are examples of such bridges.
Evolution
When thinking about how Apple’s ecosystem will evolve, the focus shouldn’t be on which new devices or services Apple can come up with, but rather on how Apple can offer new experiences to its customers. The blueprint for creating such experiences is already known: leveraging control over hardware, software, and services.
Technology’s battle lines are currently being redrawn with the goal being to capture the most valuable real estate in our lives: our health, homes, and transportation. Bets on software that completely reimagines the way we approach these verticals will likely prove to be good bets. Timing remains the big unknown.
This raises a question: How will Apple approach new verticals and industries? Would Apple attempt to recreate entirely new device lineups for each industry? Will The Grand Unified Theory of Apple Products be torn apart?
Instead of selling a $80,000 electric car or moving head-first into selling a range of first-party smart home hardware, Apple’s current ecosystem provides clues as to how the company can approach these new industries.
The point of Apple entering transportation wouldn’t be to sell cars, mopeds, or bicycles. Instead, it would be to sell experiences that Apple customers can consume on the road.
The point of Apple moving deeper into smart homes wouldn’t be to sell a plethora of small home gadgets and trinkets, some of which may require an electrician to install. Instead, it would be to sell experiences that Apple customers can consume in the home.
Apple developing an autonomous car remains difficult for many to wrap their minds around. The idea of Apple one day getting into housing is still considered a fantasy by most. However, such ideas make a lot of sense when thinking about how we consume experiences during the day.
An autonomous car is nothing more than a room on wheels. A house is a series of rooms connected to each other. With each, Apple would be looking to create environments that can support new experiences.
This brings us back to Apple’s current suite of products and services. It is incorrect to assume that Apple entering new industries would result in the company throwing its current products out the window. Instead, those tools stand to play major roles in delivering experiences in new industries.
Apple’s interest with Project Titan isn’t to beat or copy Tesla, but rather to figure out a way to have personal gadgets provide compelling experiences on the road. Such experiences could include Apple Glasses being used to find the right autonomous Apple Car to enter while Apple Watches can be used as identification for entry. Once inside the vehicle, the digital assistant found on the wrist or in front of our eyes could then be used to convert the car’s hardware to suit our needs. A similar dynamic would be found with smart homes - relying on personal gadgets, especially wearables, to come up with premium experiences in the home. We are seeing the early stages of this with products like HomePod and the way the device can be seamlessly used with Apple Watch.
The idea that Apple would enter the transportation and housing industries simply to come up with more areas for its users to engage with wearables may seem preposterous today. However, the idea that a single company would be able to deliver hundreds of billions of experiences per day by selling tools consisting of hardware, software, and services was similarly once a fantasy.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members in both written and audio forms. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
For additional discussion on this topic, check out the Above Avalon daily update from July 23rd.
Above Avalon Podcast Episode 170: Pulling Away From the Competition
In episode 170, Neil examines how Apple is pulling away from the competition to a degree that we haven’t ever seen before. Given how we are just now entering the wearables era, implications of this shift will be measured in the coming decades, not years. Additional topics include WWDC 2020, Apple’s revised product strategy, the competitive landscape, and Apple’s lead in wearables.
To listen to episode 170, go here.
The complete Above Avalon podcast episode archive is available here.
Apple Is Pulling Away From the Competition
For the second year in a row, Apple held a developers conference that should frighten its competitors. Relying on a nearly maniacal obsession with the user experience, Apple is removing oxygen from every market that it plays in. At the same time, the tech landscape is riddled with increasingly bad bets, indifference, and a lack of vision. Apple is pulling away from the competition to a degree that we haven’t ever seen before. Given how we are just now entering the wearables era, implications of this shift will be measured in the coming decades, not years.
WWDC 2020
It speaks volumes that Apple held its strongest WWDC in years during the middle of a pandemic while two of its largest competitors, Google and Facebook, decided to skip their annual developers conferences. Just a few years ago, fortunes were reversed. Apple was coming under fire for WWDCs that appeared to be more reactionary to Google, Facebook, and Samsung. Apple was also struggling to contain growing unrest among its pro users who were tempted by Microsoft Surface hardware.
What changed?
The last two WWDCs stood out for two reasons:
A revised Apple product strategy. A few years ago, Apple was most aggressive with products capable of making technology more relevant and personal (iPhone and Apple Watch). As shown in Exhibit 1, in the pull strategy, the Apple Watch and iPhone were Apple’s clear priorities while the iPad, Mac portables, and Mac desktops ended up facing a battle for management attention as if they were located at the end of the rope that was Apple management was pulling.
Apple changed from a “pull” strategy in which some products like the iPad and Mac seemed to be having a hard time keeping up to a push strategy characterized by every major product category moving forward simultaneously. This shift appears to have been born in 2017, which would explain why we are still seeing the initial fruit of the effort. The iPad and Mac product categories have benefited the most from this revised “push” product strategy with more frequent and noteworthy updates.
Exhibit 1: Apple’s Changing Product Strategy
Apple has doubled down on its unique interpretation of innovation. During his opening remarks at the iPhone and Apple Watch event last September, Tim Cook said that Apple sells tools containing "[i]nnovations that enrich people's lives to help them learn, create, work, play, share, and stay healthy." Instead of defining innovation as either being first or doing something different, Apple looks at innovation as something that improves customers’ lives. A major consequence of this has been software and hardware releases that have prioritized feature quality over quantity. This year’s WWDC came in a full 20% shorter than previous keynotes. While having a digital format helped cut down on the timing due to quicker transitions, no clapping etc., there were also fewer new features announced. However, the features that were announced contained more significance when it comes to pushing the user experience forward.
A Stronger Apple
Unfortunately for Apple competitors, the combination of a revised product strategy and unique definition of innovation didn’t just make for strong WWDC keynotes. Consumers are noticing and wanting what Apple is selling. Consider the following trends:
Apple hasn’t just held its own in the smartphone space but rather is continuing to take share from Android. Of all the smartphone manufacturers, Apple saw the largest sales share increase in the smartphone industry last quarter, and that was during a pandemic.
Apple is adding approximately 20 million new iPad users per year despite the iPad being 10 years old and already having an installed base exceeding 300 million users.
Apple’s oldest major product category, the Mac, is adding 10 million new users per year.
Apple Watch and AirPods are quickly approaching 100 million user bases each.
Apple users are paying for 518 million subscriptions across Apple’s platforms, which is up 126 million in just a year.
All of the preceding items amount to an Apple ecosystem gaining momentum. A different way of highlighting Apple’s growing ecosystem over the past 10 years is to look at the number of people using at least one Apple device. As shown in Exhibit 2, Apple’s installed base recently surpassed a billion users.
Exhibit 2: Apple Installed Base (Number of Users)
While new user growth rates have slowed, Apple is still bringing tens of millions of users into the fold. Due to Apple’s views regarding innovation and its focus on the user experience, once someone enters the Apple ecosystem, odds are good that customer will remain in the ecosystem.
This is why one subtheme from last week’s WWDC keynote flew under the radar. (My complete WWDC 2020 review is available here for Above Avalon members.) It’s not just about Apple pushing multiple product categories forward at the same time. Instead, it’s about adding cohesiveness and commonality between product categories. Apple is making it easier for people to buy multiple Apple devices. As users move deeper into the Apple ecosystem, satisfaction and loyalty rates stand to go even higher. The end result is that Apple’s billion users aren’t just any billion users. Instead, they are a billion users less likely to use non-Apple devices and services going forward. For the competition, this is a highly concerning development.
More worrying for competitors, Apple is still in the early stages of bringing its users deeper into the ecosystem. According to my estimate, approximately 50% of Apple users still own just one Apple device: an iPhone. This group serves as a prime market for products like the iPad, Apple Watch, AirPods, and various Apple services. In a few years, that percentage may decline to something more like 30%. Such a development will remove much of the remaining oxygen from the markets Apple plays in.
Competition Is Weakening
While Apple sails forward with a strengthening ecosystem made possible by a clear product vision and a functioning organizational structure that prioritizes design (i.e. the user experience), the competition is rudderless.
Apple competitors have been striking out with one bad product bet after another. Few have long-term vision as to where computing is headed. Consider the following events, developments, and observations. By no means is this an inclusive list.
Samsung remains rudderless from a product vision perspective. With no clear direction as to where to go, the company aimlessly launches new products and features for no other reason than to say they are first. The strategy is no different than throwing things against the wall and hoping something sticks. Even worse, the products and features that Samsung is announcing aren’t even ready for public usage.
Google continues to prioritize technology over design. While new software features may seem compelling on paper, the lack of attention given to the user experience quickly becomes apparent. It has also become difficult to miss the growing enthusiasm gap between Android and iOS. On the hardware front, Google is struggling to match such efforts with its ambient computing future (which doesn’t make much sense to me).
Amazon’s massive bet on voice with Alexa and Echo was the wrong one. The stationary smart speaker space was a mirage. Amazon should have instead bet on wearables with voice as a user input. However, the company doesn’t have the corporate culture to excel with computers worn on the body.
Microsoft appears to be running into growing trouble with the consumer when it comes to Surface. What had been a genuine chance to rip into the iPad and Mac stronghold due to growing user unrest looks to have been successfully crushed by Apple. Microsoft Surface revenue is increasingly being driven by commercial clients (i.e. Microsoft is taking share from its OEMs rather than Apple).
Facebook ended up placing the wrong social bet. Instead of going after our closest social network, Facebook evolved to offer a curated version of the web via the News Feed. The company’s pivot back to a privacy-focused social platform built around messaging emphasizes this wrong bet. A message sent through Apple’s Messages is a message not sent through a Facebook property.
Snap, the company considered to have the best odds of competing with Apple on AR, botched its first major foray into AR hardware with Spectacles. The company has backed itself in a corner by management’s refusal, and then failure, to appeal to older demographics. This will serve as a headwind for mass market AR successes.
Spotify was not able to prevent Apple Music from gaining critical mass despite Apple Music not having a free tier. The same is now taking place with Netflix, which is unable to stop new entrants into paid video streaming from gaining traction. This ends up diffusing near universal praise in the press for first movers.
For an industry that was expected to put Apple in its place, that sure is a lot of fails, flops, and disappointments. When looking outside the U.S., the overall picture isn’t dramatically different. While some companies still have pockets of strength where Apple is not a major player, in geographies Apple is playing in, the company continues to see growing ecosystem momentum while the competition flounders. The number of paid subscriptions being run through Apple’s platform points to increased services and app adoption outside the U.S.
The never-ending tales of Apple being crushed by the local competition in China have been met with Apple seeing existing users move deeper into the ecosystem as measured by App Store, iPad, and wearables momentum. Huawei’s struggles in Europe appear to be benefiting Apple at the premium end of the market.
Changing Narrative
If there was still doubt about Apple’s momentum in the marketplace, one doesn’t need to look any further than the dramatic change in narrative facing Apple in the press.
For years, Apple was positioned as one iPhone update away from implosion. Low market and sales share were paraded around as signs of an incompetent product strategy. Simply put, Apple was framed as being weak and vulnerable, dependent on revenue sources that could disappear overnight due to consumers fleeing to the competition.
The narrative has completely shifted. The press is now infatuated with Apple’s power, its ironclad grip over the App Store, and the idea that Apple users are stuck or imprisoned in a massive walled garden where things like iMessage, Apple Watches, and AirPods force people to remain within Apple’s walls. Government regulators are viewed as the only entity capable of protecting Apple users from Apple.
If competitors actually believe this narrative, they are setting themselves for more failure. Thinking that Apple users are somehow being forced against their will to buy products like Apple Watches and AirPods is nothing more than looking for someone to blame for market failures when the problem is found internally with a bad vision, inadequate corporate culture, and lack of understanding as to what makes Apple unique.
Risks
On a list of risk factors facing Apple, greater regulation is far from the top. The same can be said about things like App Store policies and employee retention. While these items make for juicy headlines capable of grabbing people’s attention, they won’t play a major role in Apple’s future. Instead, Apple is where it is today by saying “no” more than “yes.” By remaining focused on making technology more personal, which is inherently about using a design-led culture to push the user experience, Apple is able to develop a dynamic, yet nimble, ecosystem of tools that people are willing to pay for. lf it were to lose focus, Apple would move that much closer to its competitors.
Apple ends up being its toughest competitor as it releases products that surpass the previous version. This is where betting on the user experience and taking a unique stance on innovation is critical.
Next Ten Years
When the iPhone was unveiled in 2007, Steve Jobs claimed that Apple had a five-year head start against the competition. He ended up being mostly right. By 2012, Samsung and Google were shipping credible iPhone alternatives, thanks partially to ruthless copying that led to time in the courtroom.
With wearables, my thinking has been that Apple has a lead that is closer to 10 years. This estimate reflects not just software or hardware advantages, but also the byproduct of Apple controlling both items and its resulting achievements with custom silicon.
As time passes, Apple has been facing less competition in wearables. This is remarkable considering how Apple Watch has already ushered in the next paradigm shift in computing. We are seeing the future today. Yet most companies either don’t see it or even worse, see it but are unable to respond.
Giving Apple a 10-year head start against the competition with wearables may end up giving too much credit to the competition. Excelling in wearables requires a corporate culture, product development process, and business model that few companies other than Apple possess. In many ways, Apple was built to excel in wearables. Apple should probably get used to being its own toughest competitor.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
Predicting Turns on Wall Street
Wall Street got the pandemic right. Or did it? For the past two months, financial market commentators have been stumped by the stock market’s resiliency. The common refrain has been that the market is too optimistic given what seems to be crisis after crisis. With a pandemic still ongoing, Apple and a growing list of companies are trading at all-time highs. The NASDAQ just hit a record high while the S&P 500 is nearly up for the year. Fixed income markets remain shockingly robust. A closer examination of how the past three months transpired shines light on the idea that Wall Street tried to predict the pandemic’s turn without actually knowing what such a turn would look like.
Market Truths
There are two truths when it comes to how Wall Street functions:
1) Markets are forward-looking. A company’s stock price is not based on how that company performed in the past. If a company reports stellar earnings for the quarter that just ended but then reveals bankruptcy is on the horizon, the market is not going to make sure the strong results that occurred in the past are valued appropriately. Stock prices are determined by expectations of what will happen in the future, and more specifically, a company’s future cash flow stream.
Fixed income markets are based on economic trends going forward, not where the economy was in the past. Valuation multiples used for M&A are based not on how a target performed last year, but rather on expectations for future performance.
The implications found with forward-looking markets are immense. Two months ago, unemployment claims data suggested 16 million people had lost their jobs in just a three-week span. The stock market went on to register its strongest weekly performance in decades that particular week. This led to the following tweet from U.S. Congresswoman Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez:
Many looked at such juxtaposition as a sign of Wall Street’s corruption or brokenness - as if the market was actually applauding 16 million people losing jobs. This was not the case. Instead, since the market is forward-looking, the focus had already shifted to the May and June jobs reports. A more accurate tweet would have compared the market’s 11% down week in February with news of 16 million Americans losing their jobs in March.
2) Markets are comprised of participants with different perspectives and viewpoints. The idea that there is one person or entity determining whether equity markets move up or down on any given day is fantasy - something portrayed by the press in an attempt to add clarity to what is inherently a lot of unknown. Instead, financial markets are comprised of different viewpoints, often at odds with each other, that must come together so that price discovery can occur.
Contrary to what financial and business news publications would lead you to believe, it is impossible to know why stocks move up or down on any given day. In order to figure out why a stock is behaving a certain way, each market participant buying and selling shares of that stock would need to be questioned as to their reasoning and motive. Since such an activity isn’t feasible, it is impossible to know the reason(s) why a stock moves in a particular direction.
It may be easy to look at an S&P 500 price chart for the past few months and determine that Wall Street made one big bet around the end of March: that there would be a turn in the pandemic - a point at which the health crisis would bottom and then begin to improve, bringing with it better economic trends.
This would be an incorrect assessment of how the stock market, and Wall Street in general, operates.
There was never one large bet made by “the market” in March regarding the pandemic since there isn’t one market participant. Instead, there were millions, even tens of millions, of smaller predictions made. Some predictions were that the pandemic would just disappear. Others called for the pandemic to become increasingly bad as 2020 progressed.
The participants making these predictions considered asset prices and, using their own expectations of what may or may not happen, made a determination as to whether or not prices reflected their expectations. Exposure and risk appetites were then judged.
Another truth when it comes to the stock market’s performance over the past three months is that there was never one set of predictions guiding price action. It’s easy to think that the market is simply moving off of the same months-old mindset that existed in March, but that is faulty logic. The market is in a very different place today than it was just a month ago, or even a week ago for that matter. Predictions have been constantly evolving, both to the upside and downside, as new information comes to light.
Consider the following noteworthy events that occurred since the stock market bottomed in March:
End of March. It became clear that U.S. policymakers on both sides of the aisle were going to respond to the economic impact from the pandemic in a very big way.
Early April. After a shaky few weeks, fixed income markets returned to stability due, in part, to unprecedented commitments from the U.S. Fed. A wave of bankruptcies hitting major corporations that had seemed likely just a few weeks prior to this time was not going to materialize.
Mid to Late April. The 1Q20 earnings season was characterized by management commentary being more upbeat than analyst expectations. It also became clear that the pandemic was going to impact some industries more than others.
May and early June. The coronavirus epicenter in the U.S. (the NYC metro area) saw a complete turnaround on the health front with clear improvement in most coronavirus-related trends.
Early June. A surprisingly strong May jobs report reflected the positive impact from government stimulus programs and states beginning to reopen.
Market participants had plenty of opportunities to test their predictions made in March with the preceding developments and adjust viewpoints accordingly.
Business of Predicting Turns
Since the market is always forward-looking, the inherent nature of Wall Street is to be in the business of predicting turns - assessing when good economic times will turn sour and when bad economic times will turn positive. This practice was not unique to the pandemic.
Sometimes the collective nature of Wall Street’s predictions ends up being wrong. In late 2018, fears of the U.S. falling into a recession didn’t materialize. Back in late February, predictions that the pandemic would be quickly contained and not lead to major economic interruptions obviously ended up being wrong.
If consensus is wrong on a prediction turn, asset prices adjust and Wall Street participants regroup to make yet another prediction about a potential turn.
Apple as Example
This turn predicting occurs not only at the stock index level, but also at an individual company level. We can use Apple as an example.
Back in February, some market participants bet Apple would find itself in major trouble as the pandemic would impact both supply and demand. However, there were other market participants betting that Apple wasn’t going to suffer much on the supply side and demand would simply be delayed into the second half of 2020 and 2021.
How can such different viewpoints exist for the same company? It all comes down to how Apple is viewed. Looking at Apple as just an iPhone maker will lead to different predictions than will viewing Apple as a toolmaker with a billion engaged users who aren’t likely to go elsewhere for computing tools. This is often why commentary from those who don’t know much about Apple is prone to error. It may be easy and tempting to think that iPhone users will choose less expensive alternatives during a recession. However, one will be more accurate looking at the situation in terms of ecosystems and iPhone users not having much desire or incentive to leave Apple’s ecosystem.
Apple’s FY2Q20 earnings at the end of April marked a turning point as management disclosed that recent trends reflected demand improving “across the board.” A logical explanation was that government stimulus programs were starting to hit while product categories like the Mac and iPad were actually seeing improved results from developments like distance learning and people working from home.
Lessons
Is there a way to get ahead of Wall Street’s nature of predicting turns? Knowledge is power when it comes to achieving proper perspective. Less time should be given to topics like where markets may be headed or what is driving markets up and down on any given day. Both topics are bound to be guided by entertainment-led directives. Instead, time and attention should be given to people with unique perspectives that are able to analyze news events separately from daily stock price moves. These perspectives come from experts relying on years of experience in their respective field which allows historical context to be added to the news.
Caution is needed when determining where to turn for financial market news. I stopped watching CNBC during the pandemic because of inadequate coverage.
At the end of February, CNBC invited Jeremy Siegel, professor of finance at the University of Pennsylvania, to talk about the collapsing stock market at the time. Siegel, a CNBC regular, discussed how the vast majority of a stock price is not derived by earnings over the next 12 months, but instead by cash flow further out.
As shown in the video below, Siegel didn’t make a direct short-term call on either the market or the pandemic. Instead, Siegel was trying to add some calm to a market that was increasingly getting out of hand. The CNBC hosts didn’t want anything to do with Siegel’s comments.
Each of the hosts’ initial responses were to go after Siegel’s remarks and try to get him to say something more hysterical. The exchange was just one example of what ended up being weeks of fear-led coverage based on whatever the tone of the news was that morning. One day the end of the world was near, and the next day a random vaccine trial meant the market was undervalued by 30%.
Looking ahead, there isn’t going to be much change in the way financial markets are covered unless there is a fundamental change in business models. Finance news publications and outlets that are ultimately based on advertising will continue to being incentivized to get as many people as possible to click articles and watch videos. Said another way, financial news outlets will continue to do better when markets are in turmoil.
A Turn in the Pandemic?
This brings us back to the original question: Did Wall Street get the pandemic right?
While some market participants will be quick to say that their own (rosy) projections about the pandemic ended up right, the truth is that the situation was much more complicated.
My thinking is that most people probably haven’t changed their viewpoints regarding the pandemic over the past two months. Those who tended to be on the optimistic side of the spectrum remain optimistic. Those who were pessimistic, remain just as pessimistic. There is still a wide spectrum of viewpoints in this market regarding how the pandemic will trend for the rest of 2020.
What can explain the market’s strong performance over the past two months?
There were a number of factors that came together to impact equities. However, one of the more glaring changes was that calmness entered the market. The Chicago Board Options Exchange’s CBOE Volatility Index, known as simply the VIX, is commonly referred to as the market’s fear gauge. It measures the expected or future volatility of the market based on S&P index options. The higher the VIX, the greater the level of fear. The VIX has collapsed over the past three months (although it remains elevated).
In February and early March, the market saw the most volatile price action it has seen since the 1987 crash. Simply put, humans don’t react well to that kind of volatility. Over the subsequent three months, the news flow has in many ways allowed a level of calm to return to the markets.
Not having debt markets implode will have a material impact on one’s view on equities.
Having some of the largest companies in the world talk about a bottoming in demand in April will get attention.
Signs of improvement in the employment situation due to stimulus programs and states reopening won’t go unnoticed.
All of those developments amount to stability reentering the market. One can still have a negative viewpoint of the health impact arising from the pandemic. But when it comes to transcribing that viewpoint into thoughts about asset prices and equity valuations, emotion inevitably plays a major role.
Predicting turns on Wall Street ends up being about predicting when calmness will enter and leave the market - when market participants will be guided more by emotions and feelings or numbers and facts. Given the way humans behave, we can have a high degree of confidence there will be plenty of future turns to predict on Wall Street. In some ways, that’s why Wall Street exists in the first place - for there to be a marketplace where the economic and financial ups and downs associated with human emotion can be allowed to play themselves out.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.
Above Avalon Podcast Episode 168: The Paid Membership Model
This past week marked the fifth anniversary of Neil launching Above Avalon membership. Above Avalon continues to thrive with a sustainable business model based solely on paid memberships. In episode 168, Neil gives a behind-the-scenes look at Above Avalon’s business model. Additional topics include: Above Avalon’s history, Neil’s “secrets” to success, and his largest challenges found with a paid membership model.
To listen to episode 168, go here.
The complete Above Avalon podcast episode archive is available here.
Above Avalon Podcast Episode 162: The Apple Question
At the start of a new year, there is less value found in coming up with predictions than there is in looking at questions facing the company. In episode 162, Neil goes over his list of questions for Apple in 2020, and the discussion culminates with one overarching question that covers Apple’s largest challenge and opportunity. Additional topics include why predictions contain so little value, the number of Apple users, and Apple in emerging markets.
To listen to episode 162, go here.
The complete Above Avalon podcast episode archive is available here.
The Big Question Now Facing Apple
Predictions are nothing more than attempts at manufacturing clarity for what is inherently a sea of unknown. With New Year predictions, two things need to happen. The person issuing the prediction needs to come up with what may happen, and the predicted event has to occur within an arbitrary time period. The probability of finding value in such an exercise is low.
Instead of coming up with predictions for Apple at the start of a new year, there is value found in embracing the unknown and looking at questions facing the company. This has led to my annual tradition of coming up with a set of questions facing Apple at the start of a new year. The irony found with questions is that asking the right ones is equivalent to coming up with a surf board for successfully catching waves in the sea of unknown.
Previous year’s questions are found below:
Questions for Apple in 2020
The topics that serve as source material for Apple questions in 2020 can be grouped into two buckets: growth initiatives and asset base optimization.
Growth Initiatives
iPhone Business. The narrative facing the iPhone business has been off the mark for years. Skepticism and cynicism has continued to mask what has been a resilient business. There is now too much talk of 5G kicking off some kind of mega upgrade iPhone cycle. Such a focus ignores what is ultimately taking place with the iPhone: The business is maturing. This presents a set of challenges that will require a fine-tuning of strategy. This involves changes to the device lineup, release schedule, pricing, and feature set.
Paid Content Distribution. Following a very busy 2019 for Apple’s content distribution arm, all eyes are on whether or not Apple will bundle its new paid content services. Ultimately, bundling is a tool that Apple has at its disposal to support a weaker service while increasing the stickiness found with its services.
Wearables. Apple’s wearables business is a runaway train with the company selling approximately 65M wearable devices in FY2019. Based on my Apple Watch installed base estimate (available here), just 7% of iPhone users own an Apple Watch. Similar ownership percentages are found with AirPods despite the product having been in the market for less time. The question isn’t if Apple wearables momentum will continue but instead how fast will adoption grow.
Margins. Apple follows a “revenue and gross margin optimization” pricing strategy. This has led to Apple’s products gross margin percentage declining by 10% over the past two years while products gross margin dollars have declined by only 2%. Apple is willing to let products gross margin percentages decline (via lower product prices and higher cost of goods sold relative to revenue) if it results in stronger customer demand for those products. Attention will be placed at determining the level at which Apple product pricing is too low in order to maximize gross profit dollars.
R&D. There have been two general themes found with Project Titan and Apple’s efforts related to developing a pair of AR glasses: 1) Continued progress and 2) Extended timelines.
Asset Base Optimization
Leadership. With Jeff Williams officially serving as the link between Apple’s design team and the rest of Tim Cook’s inner circle, it will be interesting to see if Apple makes any refinements to its leadership structure.
China. The boogeyman known as U.S. / China trade has been put to bed, for now. With rhetoric having been dialed back in a very big way, attention will shift to the various decisions Apple still has to make regarding its long-term approach to China. The company can continue to rely heavily on China for its supply chain and manufacturing apparatus, accelerate a diversification strategy away from the country, or follow more of a status quo approach that recognizes the benefits (and weaknesses) of being so dependent on one country.
Capex. In FY2019, Apple reported just $7.6 billion of capital expenditures (capex). This was a significant drop from the $16.7 billion of capex in 2018. The most likely reason for the decline in capex was a decline in tooling and manufacturing machinery. The company also slowed spending on corporate facilities. By not providing capex guidance for FY2020, the variable is accompanied by a greater level of intrigue as to what it means about Apple’s near-term product pipeline.
Capital Return. Apple shares were up 89% in 2019, exceeding the S&P 500’s 31% gain. For the first time with Tim Cook as CEO, Apple shares now trade at a premium to the overall market when looking at forward price-to-earnings multiples. This has led some financial writers to call for Apple to slow the pace of buyback and instead push a larger increase in the quarterly cash dividend. In the event that Apple’s market value exceeds intrinsic value, it’s not clear how Apple would remove tens of billions of dollars of excess cash still on the balance sheet in addition to nearly $60 billion of free cash flow generated per year. Special dividends aren’t great from a tax perspective while there are limitations found with simply funneling all of the excess cash into quarterly cash dividends.
The Big Question
Taking a closer look at the preceding list of unknowns facing Apple, the product categories that have served as the primary engines for Apple’s new user growth are quickly maturing while new product categories have been more ARPU (average revenue per user) drivers. There are more than 500 million people who own just one Apple product: an iPhone. This group represents a prime target market for Apple when selling additional tools. Apple is ending one growth phase and is about to enter into a new one.
Exhibit 1 shows the growth trajectory for the number of Apple users, also referred to as Apple’s installed base, over the past 10 years. Based on my estimates, the Apple installed base grew from approximately 90 million people at the end of 2009 to a little more than a billion people at the end of 2019. Apple’s new user growth has slowed dramatically. Thanks primarily to the iPhone, Apple saw spectacular new user growth in the range of 25% to 60% in the early to mid-2010s. More recently, new user growth has been trending in the mid single-digit range.
Exhibit 1: Apple Installed Base (Number of Users)
The methodology and math used to reach my estimate for the number of Apple users is available for Above Avalon members here.
Reaching a billion users is quite the accomplishment for Apple considering how the company doesn’t give away its products for free. It’s one thing to reach a billion users with a “free” service. However, to get a billion people to pay directly for a service or tool is an entirely different thing.
When thinking about Apple’s future, the big question facing the company isn’t about how it will sell additional tools to its existing user base. Instead, the major unknown facing Apple is found with management’s ability to continue expanding its installed base. This raises one overarching question that covers Apple’s largest challenge and opportunity:
How will Apple find its next billion users?
It may be tempting to classify Apple’s first billion users as the “easy” growth or low-hanging fruit. In reality, those billion users primarily came from the premium segments of the various industries that Apple competes in. This means that to find the next billion users, Apple will inevitably need some strategy adjustments.
The Strategy for the Next Billion
The major building blocks for Apple’s plan to find its next billion users are already in place. Apple will come up with tools capable of making technology more personal. This pursuit will involve new user interfaces and inputs that allow people to get more out of technology without having technology take over people’s lives.
Taking a look at the geographical makeup of Apple’s current installed base, developed markets still contain plenty of new users for Apple to target. However, the potential found with emerging markets is a completely different story. Indonesia, Brazil, the Philippines, and Vietnam have a total population that is twice that of the U.S. Meanwhile, there are more people in China and India (2.6 billion) than the next 20 most populated countries combined.
It may be easy to think that Apple can just cut product pricing in order to grab its next billion users. However, the situation ends up being more complicated. Socio-economic trends will contribute to tens of millions of people moving into Apple’s addressable market each year. In addition, relying on the gray market for allowing gently-used Apple products to flow to lower price segments is a more effective strategy for Apple. Not only does the gray market reduce the need for Apple to come up with low priced products lacking in features, but Apple can also benefit from continued product focus in terms of its supply chain and manufacturing apparatus.
As for some of the granular initiatives that stand to promote continued growth in Apple’s installed base:
A truly independent Apple Watch. Advancements such as a truly independent Apple Watch that doesn’t require another Apple device to activate and use will expand the device’s addressable market by nearly four times overnight.
Continuing to run forward with wearables. New product categories that allow Apple to break down the barriers between users and technology will allow the company to target a wider audience. New form factors such as glasses will be designed to make technology even more personal than what is possible with Apple Watch and AirPods.
Longer device longevity. By giving Apple devices longer lifespans via more durable hardware and additional years of software updates, devices will be able to have more owners over time. This will have a direct benefit on the gray market for Apple devices as more devices are recirculated and eventually able to reach customers in lower price segments.
Expanding device repair and support networks. Apple’s current retail store footprint is not capable of handing the additional product servicing and support associated with having another billion users in its ecosystem. This is especially true in developing markets. By building out a device repair and support network to include authorized third-parties, Apple will go a long way in ensuring the next billion users have access to many of the same experiences that are valued by Apple’s current users.
The path to two billion users won’t be easy for Apple. The trajectory may very well end up looking quite different than the path to a billion users. However, there is nothing found with Apple’s long-standing mission to create products that can change people’s lives that limits its reach to a billion people.
Listen to the corresponding Above Avalon podcast episode for this article here.
Receive my analysis and perspective on Apple throughout the week via exclusive daily updates (2-3 stories per day, 10-12 stories per week). Available to Above Avalon members. To sign up and for more information on membership, visit the membership page.